Tropisetron Facilitates Footshock Suppression of Compulsive Cocaine Seeking
- PMID: 31125405
- PMCID: PMC6754734
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyz023
Tropisetron Facilitates Footshock Suppression of Compulsive Cocaine Seeking
Abstract
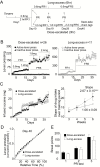
Background: The hallmark characteristics of the murine model of drug addiction include the escalation of cocaine consumption and compulsive punishment-resistant drug seeking. In this study, we evaluated the motivation for drug seeking in cocaine self-administering rats exposed to an escalated dosing regimen that endeavored to mimic the characteristic of escalating drug intake in human addicts. Tropisetron is a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist and α7-nicotinic receptor partial agonist. Utilizing rats trained on the escalated-dosing regimen, we examined the effects of tropisetron on control over compulsive drug-seeking behavior that was defined as footshock-resistant lever pressing.
Methods: Rats were trained to self-administer cocaine with incremental-infusion doses (from 0.6 to 2.4 mg/kg/infusion) across training sessions (3 h/session) or with a long-access paradigm (i.e., 0.6 mg/kg/infusion, 6 h/d training session). The drug-seeking motivations of 2 groups were estimated by the patterns of drug intake and progressive-ratio schedule. The compulsivity for drug seeking of the group with an escalated dose was further evaluated using the footshock-associated seeking-taking chain task.
Results: The rats trained on the dose-escalated protocol achieved the same levels of motivated drug seeking as those subjected to a long-access paradigm, as indicated by cocaine intake per training session and breakpoints on a progressive ratio schedule. Tropisetron attenuated compulsive behavior of rats when pressing of the seeking lever potentially led to footshock. Intriguingly, tropisetron did not change the motivation to seek cocaine when footshock was absent. Tropisetron had no effect on locomotor activities or saccharin self-administration.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate that tropisetron restored control over compulsive cocaine seeking, and they indicate that 5-HT3/α7-nicotinic receptors may be potential therapeutic targets for relieving compulsive drug seeking.
Keywords: compulsive cocaine seeking; drug addiction; footshock; self-administration; tropisetron.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Random interval schedule of reinforcement influences punishment resistance for cocaine in rats.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2024 Sep;213:107961. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2024.107961. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2024. PMID: 39025429
-
High and escalating levels of cocaine intake are dissociable from subsequent incentive motivation for the drug in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018 Jan;235(1):317-328. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4773-8. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018. PMID: 29085961
-
Differential roles of the prefrontal cortical subregions and basolateral amygdala in compulsive cocaine seeking and relapse after voluntary abstinence in rats.Eur J Neurosci. 2013 Oct;38(7):3018-26. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12289. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23815783 Free PMC article.
-
Conflation of cocaine seeking and cocaine taking responses in IV self-administration experiments in rats: methodological and interpretational considerations.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013 Nov;37(9 Pt A):2026-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.04.017. Epub 2013 May 10. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013. PMID: 23669047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rodent models for compulsive alcohol intake.Alcohol. 2014 May;48(3):253-64. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Alcohol. 2014. PMID: 24731992 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Animal Models of the Behavioral Symptoms of Substance Use Disorders.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021 Aug 2;11(8):a040287. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a040287. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021. PMID: 32513674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of glutamate homeostasis in the nucleus accumbens by astrocytic CB1 receptors and its role in cocaine-motivated behaviors.Addict Neurosci. 2022 Sep;3:100022. doi: 10.1016/j.addicn.2022.100022. Epub 2022 May 21. Addict Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36419922 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of multitarget drugs on the expression of cocaine-induced locomotor sensitization in male rats: A comparative study.Heliyon. 2024 May 1;10(9):e29979. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29979. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38726128 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the 5-HT2C receptor drugs RO 60-0175, WAY 161503 and mirtazepine in a preclinical model of comorbidity of depression and cocaine addiction.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Feb;75(1):99-118. doi: 10.1007/s43440-022-00428-2. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36374478 Free PMC article.
-
Punishment resistance for cocaine is associated with inflexible habits in rats.Addict Neurosci. 2024 Jun;11:100148. doi: 10.1016/j.addicn.2024.100148. Epub 2024 Jan 27. Addict Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38859977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed SH, Koob GF (1998) Transition from moderate to excessive drug intake: change in hedonic set point. Science 282:298–300. - PubMed
-
- Allain F, Bouayad-Gervais K, Samaha AN (2018) High and escalating levels of cocaine intake are dissociable from subsequent incentive motivation for the drug in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 235:317–328. - PubMed
-
- Beinat C, Banister SD, Herrera M, Law V, Kassiou M (2015) The therapeutic potential of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7 nAChR) agonists for the treatment of the cognitive deficits associated with schizophrenia. CNS Drugs 29:529–542. - PubMed
-
- Callahan PM, Bertrand D, Bertrand S, Plagenhoef MR, Terry AV Jr (2017) Tropisetron sensitizes α7 containing nicotinic receptors to low levels of acetylcholine in vitro and improves memory-related task performance in young and aged animals. Neuropharmacology 117:422–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

