LIF, a Novel Myokine, Protects Against Amyloid-Beta-Induced Neurotoxicity via Akt-Mediated Autophagy Signaling in Hippocampal Cells
- PMID: 31125414
- PMCID: PMC6545540
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyz016
LIF, a Novel Myokine, Protects Against Amyloid-Beta-Induced Neurotoxicity via Akt-Mediated Autophagy Signaling in Hippocampal Cells
Abstract
Background: Leukemia inhibitory factor, a novel myokine, is known to be associated with neural function, but the underlying molecular mechanism remains unclear.
Methods: HT-22 mouse hippocampal cells, primary hippocampal cells, and Drosophila Alzheimer's disease model were used to determine the effect of leukemia inhibitory factor on neurons. Immunoblot analysis and immunofluorescence method were used to analyze biological mechanism.
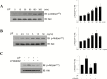
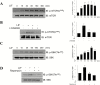
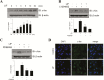
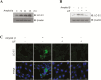
Results: Leukemia inhibitory factor increased Akt phosphorylation in a phosphoinositide-3-kinase-dependent manner in hippocampal cells. Leukemia inhibitory factor also increased the phosphorylation of the mammalian target of rapamycin and the downstream S6K. Leukemia inhibitory factor stimulated the phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription via extracellular signal-regulated kinases. Leukemia inhibitory factor increased c-fos expression through both Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinases. Leukemia inhibitory factor blocked amyloid β-induced neural viability suppression and inhibited amyloid β-induced glucose uptake impairment through the block of amyloid β-mediated insulin receptor downregulation. Leukemia inhibitory factor blocked amyloid β-mediated induction of the autophagy marker, microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3. Additionally, in primary prepared hippocampal cells, leukemia inhibitory factor stimulated Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase, demonstrating that leukemia inhibitory factor has physiological relevance in vivo. Suppression of the autophagy marker, light chain 3II, by leukemia inhibitory factor was observed in a Drosophila model of Alzheimer's disease.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate that leukemia inhibitory factor protects against amyloid β-induced neurotoxicity via Akt/extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mediated c-fos induction, and thus suggest that leukemia inhibitory factor is a potential drug for Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Akt; Alzheimer’s disease; LIF; autophagy; mTOR; myokine.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Schizandrol A protects against Aβ1-42-induced autophagy via activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in SH-SY5Y cells and primary hippocampal neurons.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020 Sep;393(9):1739-1752. doi: 10.1007/s00210-019-01792-2. Epub 2020 Jan 4. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31900522
-
IGF-1 alleviates NMDA-induced excitotoxicity in cultured hippocampal neurons against autophagy via the NR2B/PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2014 Nov;229(11):1618-29. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24607. J Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24604717
-
The Interplay of Akt and ERK in Aβ Toxicity and Insulin-Mediated Protection in Primary Hippocampal Cell Culture.J Mol Neurosci. 2015 Nov;57(3):325-34. doi: 10.1007/s12031-015-0622-6. Epub 2015 Aug 13. J Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26266487
-
The PI3K/Akt signaling axis in Alzheimer's disease: a valuable target to stimulate or suppress?Cell Stress Chaperones. 2021 Nov;26(6):871-887. doi: 10.1007/s12192-021-01231-3. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2021. PMID: 34386944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolism: A Novel Shared Link between Diabetes Mellitus and Alzheimer's Disease.J Diabetes Res. 2020 Jan 29;2020:4981814. doi: 10.1155/2020/4981814. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 32083135 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effect of leukemia inhibitory factor on the retinal injury induced by acute ocular hypertension in rats.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Nov 22;25(1):19. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11717. eCollection 2023 Jan. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 36561619 Free PMC article.
-
Systems Genetics and Systems Biology Analysis of Paraquat Neurotoxicity in BXD Recombinant Inbred Mice.Toxicol Sci. 2020 Jul 1;176(1):137-146. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfaa050. Toxicol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32294219 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy and apoptosis cascade: which is more prominent in neuronal death?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec;78(24):8001-8047. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04004-4. Epub 2021 Nov 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34741624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetically proxied IL-6 signaling and risk of Alzheimer's disease and lobar intracerebral hemorrhage: A drug target Mendelian randomization study.Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2024 Aug 27;10(3):e70000. doi: 10.1002/trc2.70000. eCollection 2024 Jul-Sep. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2024. PMID: 39206334 Free PMC article.
-
MED12 mutation induces RTK inhibitor resistance in NSCLC via MEK/ERK pathway activation by inflammatory cytokines.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Aug 20;82(1):314. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05791-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40833497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arida RM, Cavalheiro EA, da Silva AC, Scorza FA (2008) Physical activity and epilepsy: proven and predicted benefits. Sports Med 38:607–615. - PubMed
-
- Bilak MM, Corse AM, Bilak SR, Lehar M, Tombran-Tink J, Kuncl RW (1999) Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) protects motor neurons from chronic glutamate-mediated neurodegeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58:719–728. - PubMed
-
- Brinsden PR, Alam V, de Moustier B, Engrand P (2009) Recombinant human leukemia inhibitory factor does not improve implantation and pregnancy outcomes after assisted reproductive techniques in women with recurrent unexplained implantation failure. Fertil Steril 91:1445–1447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

