Incorporation of the anteroposterior lumbar radiographs in the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score improves detection of radiographic spinal progression in axial spondyloarthritis
- PMID: 31126334
- PMCID: PMC6533656
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-019-1913-z
Incorporation of the anteroposterior lumbar radiographs in the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score improves detection of radiographic spinal progression in axial spondyloarthritis
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the performance of the extended modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS) incorporating information from anteroposterior (AP) lumbar radiographs as compared to the conventional mSASSS in detection of radiographic spinal progression in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) METHODS: A total of 210 patients with axSpA, 115 with radiographic axSpA (r-axSpA), and 95 with non-radiographic axSpA (nr-axSpA), from the GErman SPondyloarthritis Inception Cohort (GESPIC), were included in the analysis based on the availability of spinal radiographs (cervical spine lateral, lumbar spine lateral, and AP views), at baseline and year 2. Two trained readers independently scored lateral cervical and lumbar spine images according to the mSASSS system (0-3 per vertebral corner, 0-72 in total). In addition, all vertebral corners of vertebral bodies visible on lumbar AP radiographs (lower T12 to upper S1) were assessed according to the same scoring system that resulted in a total range for the extended mSASSS from 0 to 144. Reliability and sensitivity to detect radiographic spinal progression of the extended mSASSS as compared to the conventional mSASSS were evaluated.
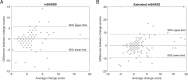
Results: The reliability of conventional and extended scores was excellent with intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) of 0.926 and 0.927 at baseline and 0.920 and 0.933 at year 2, respectively. The mean ± SD score for mSASSS and extended mSASSS at baseline were 4.25 ± 8.32 and 8.59 ± 17.96, respectively. The change score between baseline and year 2 was 0.73 ± 2.34 and 1.19 ± 3.73 for mSASSS and extended mSASSS, respectively. With the extended mSASSS, new syndesmophytes after 2 years were detected in 4 additional patients, new syndesmophytes or growth of existing syndesmophytes in 5 additional patients, and progression by ≥ 2 points in the total score in 14 additional patients meaning a 25%, 28%, and 46% increase in the proportion of patients with progression according to the respective definition as compared to the conventional score.
Conclusions: Incorporation of lumbar AP radiographs in the assessment of structural damage in the spine resulted into detection of additional patients with radiographic spinal progression not captured by the conventional mSASSS score.
Keywords: Axial spondyloarthritis; Radiographic spinal progression; Radiographs; X-rays; mSASSS.
Conflict of interest statement
ML: none declared
VRR: consulting fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria from AbbVie, MSD, and Novartis
IR: none declared
JS: consulting fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria from AbbVie, Janssen, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB
HH: consulting fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria from AbbVie, Janssen, MSD, and Novartis
MR: consulting fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria AbbVie, BMS, Celgene, Chugai, Eli Lilly, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB
DP: consulting fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria from AbbVie, BMS, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spinal radiographic progression in axial spondyloarthritis and the impact of classification as nonradiographic versus radiographic disease: Data from the Swiss Clinical Quality Management cohort.PLoS One. 2020 Mar 20;15(3):e0230268. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230268. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32196530 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of radiographic sacroiliitis in anteroposterior lumbar vs conventional pelvic radiographs in axial spondyloarthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021 Jan 5;60(1):269-276. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa260. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021. PMID: 32710108
-
Relevance of structural damage in the sacroiliac joints for the functional status and spinal mobility in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: results from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Oct 24;19(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1453-3. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29065931 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of the spondyloarthritis radiography module for calibration of readers using the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014 Jan;66(1):55-62. doi: 10.1002/acr.22083. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014. PMID: 23926089 Review.
-
Modified stoke ankylosing spondylitis spinal score as an outcome measure to assess the impact of treatment on structural progression in ankylosing spondylitis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019 Mar 1;58(3):388-400. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key128. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 29860356 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Navigating the Factors Affecting Functional Impairment in Spondyloarthritis.Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2024 May;24(2):235-242. doi: 10.18295/squmj.3.2024.023. Epub 2024 May 27. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2024. PMID: 38828242 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained low disease activity measured by ASDAS slow radiographic spinal progression in axial spondyloarthritis patients treated with TNF-inhibitors: data from REGISPONSERBIO.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Jan 21;24(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s13075-021-02695-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35063018 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Poddubnyy D, Listing J, Haibel H, Knuppel S, Rudwaleit M, Sieper J. Functional relevance of radiographic spinal progression in axial spondyloarthritis: results from the GErman SPondyloarthritis Inception Cohort. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2018;57(4):703–711. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex475. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials