Candidalysin activates innate epithelial immune responses via epidermal growth factor receptor
- PMID: 31127085
- PMCID: PMC6534540
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09915-2
Candidalysin activates innate epithelial immune responses via epidermal growth factor receptor
Abstract
Candida albicans is a fungal pathobiont, able to cause epithelial cell damage and immune activation. These functions have been attributed to its secreted toxin, candidalysin, though the molecular mechanisms are poorly understood. Here, we identify epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) as a critical component of candidalysin-triggered immune responses. We find that both C. albicans and candidalysin activate human epithelial EGFR receptors and candidalysin-deficient fungal mutants poorly induce EGFR phosphorylation during murine oropharyngeal candidiasis. Furthermore, inhibition of EGFR impairs candidalysin-triggered MAPK signalling and release of neutrophil activating chemokines in vitro, and diminishes neutrophil recruitment, causing significant mortality in an EGFR-inhibited zebrafish swimbladder model of infection. Investigation into the mechanism of EGFR activation revealed the requirement of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), EGFR ligands and calcium. We thus identify a PAMP-independent mechanism of immune stimulation and highlight candidalysin and EGFR signalling components as potential targets for prophylactic and therapeutic intervention of mucosal candidiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

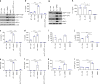
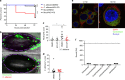


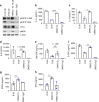
References
-
- Brown, G. D., Denning, D. W. & Levitz, S. M. Tackling human fungal infections. Science336, 647 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R15 AI094406/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE022550/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DE022550/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- MC_EX_MR/K015591/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M011372/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_16048/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R15 AI133415/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- BB/G006911/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/N014677/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/J008303/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

