Selective binding of the PHD6 finger of MLL4 to histone H4K16ac links MLL4 and MOF
- PMID: 31127101
- PMCID: PMC6534582
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10324-8
Selective binding of the PHD6 finger of MLL4 to histone H4K16ac links MLL4 and MOF
Abstract
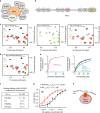
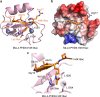
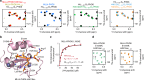
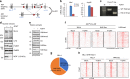
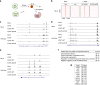
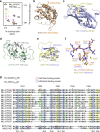
Histone methyltransferase MLL4 is centrally involved in transcriptional regulation and is often mutated in human diseases, including cancer and developmental disorders. MLL4 contains a catalytic SET domain that mono-methylates histone H3K4 and seven PHD fingers of unclear function. Here, we identify the PHD6 finger of MLL4 (MLL4-PHD6) as a selective reader of the epigenetic modification H4K16ac. The solution NMR structure of MLL4-PHD6 in complex with a H4K16ac peptide along with binding and mutational analyses reveal unique mechanistic features underlying recognition of H4K16ac. Genomic studies show that one third of MLL4 chromatin binding sites overlap with H4K16ac-enriched regions in vivo and that MLL4 occupancy in a set of genomic targets depends on the acetyltransferase activity of MOF, a H4K16ac-specific acetyltransferase. The recognition of H4K16ac is conserved in the PHD7 finger of paralogous MLL3. Together, our findings reveal a previously uncharacterized acetyllysine reader and suggest that selective targeting of H4K16ac by MLL4 provides a direct functional link between MLL4, MOF and H4K16 acetylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK071900/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)/International
- R01 GM125195/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA129325/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)/International
- R01 GM100907/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM126900/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)/International
- P30 CA016086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM106416/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)/International
- R01 DK071900/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM106416/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129325/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM124736/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)/International
- R35 GM126900/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM100907/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)/International
- GM125195/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)/International
- R01 CA204020/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM124736/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

