Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells
- PMID: 31127148
- PMCID: PMC6755964
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-019-0490-0
Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells
Abstract
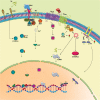
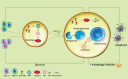
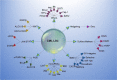
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is caused by BCRABL1 in a cell with the biological potential, intrinsic or acquired, to cause leukemia. This cell is commonly termed the CML leukemia stem cell (LSC). In humans a CML LSC is operationally-defined by ≥1 in vitro or in vivo assays of human leukemia cells transferred to immune-deficient mice. Results of these assays are sometimes discordant. There is also the unproved assumption that biological features of a CML LSC are stable. These considerations make accurate and precise identification of a CML LSC difficult or impossible. In this review, we consider biological features of CML LSCs defined by these assays. We also consider whether CML LSCs are susceptible to targeting by tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and other drugs, and whether elimination of CML LSCs is needed to achieve therapy-free remission or cure CML.
Conflict of interest statement
RPG is a part-time employee of Celgene Corp. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

