Effect of nucleolin on adriamycin resistance via the regulation of B-cell lymphoma 2 expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells
- PMID: 31127617
- PMCID: PMC6771757
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.28833
Effect of nucleolin on adriamycin resistance via the regulation of B-cell lymphoma 2 expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells
Abstract
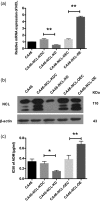
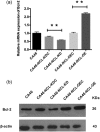
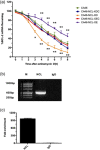
Nucleolin (NCL, C23) is an important nucleocytoplasmic multifunctional protein. Due to its multifaceted profile and high expression in cancer, NCL is considered to be a marker of drug resistance associated with chemotherapy. However, the biochemical mechanisms in which NCL suppresses drug sensitivity in several cancers have yet to be fully elucidated. This study aims to explore the effect of NCL on drug sensitivity and its potential mechanism in CA46 Burkitt's lymphoma (BL) cells. CA46 BL cells were transfected with lentiviruses carrying the NCL gene (CA46-NCL-overexpression, CA46-NCL-OE), or shRNA sequences that target the endogenous NCL gene (CA46-NCL-knockdown, CA46-NCL-KD). Adriamycin (ADM) IC50 levels for CA46-NCL-overexpressed (OE), CA46-NCL-OE control (OEC), CA46-NCL-knockdown (KD), and CA46-NCL-KD control (KDC) cells were 0.68 ± 0.06 μg/ml, 0.68 ± 0.06 μg/ml, 0.68 ± 0.06 μg/ml, and 0.30 ± 0.04 μg/ml, respectively. Apoptosis rates were significantly increased following NCL KD, whereas the opposite effect was noted in OE cells. A significant reduction of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) mRNA and protein levels in KD cells was observed, while OE cells displayed the opposite effect. The stability of Bcl-2 mRNA was influenced by NCL levels, the half-life of which was extended after NCL-OE, whereas it was reduced in KD cells. Finally, results of RNA-immunoprecipitation assays indicated that NCL could bind to Bcl-2 mRNA in CA46 cells. Taken together, these results suggested that NCL could mediate Bcl-2 expression and stability, and thus enhance ADM resistance in CA46 BL cells.
Keywords: Bcl-2; Burkitt's lymphoma; CA46; adriamycin resistance; nucleolin.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular Physiology Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Allinne, J. , Pichugin, A. , Iarovaia, O. , Klibi, M. , Barat, A. , Zlotek‐Zlotkiewicz, E. , … Vassetzky, Y. S. (2014). Perinucleolar relocalization and nucleolin as crucial events in the transcriptional activation of key genes in mantle cell lymphoma. Blood, 123(13), 2044–2053. - PubMed
-
- Amundson, S. A. , Myers, T. G. , Scudiero, D. , Kitada, S. , Reed, J. C. , & Fornace, A. J., Jr. (2000). An informatics approach identifying markers of chemosensitivity in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Research, 60(21), 6101–6110. - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay, S. , Sengupta, T. K. , Fernandes, D. J. , & Spicer, E. K. (2003). Taxol‐ and okadaic acid‐induced destabilization of bcl‐2 mRNA is associated with decreased binding of proteins to a bcl‐2 instability element. Biochemical Pharmacology, 66(7), 1151–1162. - PubMed
-
- Brockstedt, E. , Rickers, A. , Kostka, S. , Laubersheimer, A. , Dorken, B. , Wittmann‐Liebold, B. , … Otto, A. (1998). Identification of apoptosis‐associated proteins in a human Burkitt lymphoma cell line. Cleavage of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 by caspase 3. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273(43), 28057–28064. - PubMed
-
- Buggins, A. G. , & Pepper, C. J. (2010). The role of Bcl‐2 family proteins in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Leukemia Research, 34(7), 837–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

