Effect of Learning to Use a Mobility Aid on Gait and Cognitive Demands in People with Mild to Moderate Alzheimer's Disease: Part II - 4-Wheeled Walker
- PMID: 31127767
- PMCID: PMC6839464
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-181170
Effect of Learning to Use a Mobility Aid on Gait and Cognitive Demands in People with Mild to Moderate Alzheimer's Disease: Part II - 4-Wheeled Walker
Abstract
Background: Cognitive deficits and gait problems are common and progressive in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Prescription of a 4-wheeled walker is a common intervention to improve stability and independence, yet can be associated with an increased falls risk.
Objectives: 1) To examine changes in spatial-temporal gait parameters while using a 4-wheeled walker under different walking conditions, and 2) to determine the cognitive and gait task costs of walking with the aid in adults with AD and healthy older adults.
Methods: Twenty participants with AD (age 79.1±7.1 years) and 22 controls (age 68.5±10.7 years) walked using a 4-wheeled walker in a straight (6 m) and Figure of 8 path under three task conditions: single-task (no aid), dual-task (walking with aid), and multi-task (walking with aid while counting backwards by ones).
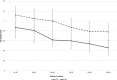
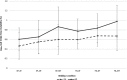
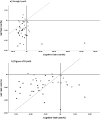
Results: Gait velocity was statistically slower in adults with AD than the controls across all conditions (all p values <0.025). Stride time variability was significantly different between groups for straight path single task (p = 0.045), straight path multi-task (p = 0.031), and Figure of 8 multi-task (0.036). Gait and cognitive task costs increased while multi-tasking, with performance decrement greater for people with AD. None of the people with AD self-prioritized gait over the cognitive task while walking in a straight path, yet 75% were able to shift prioritization to gait in the complex walking path.
Conclusion: Learning to use a 4-wheeled walker is cognitively demanding and any additional tasks increases the demands, further adversely affecting gait. The increased cognitive demands result in a decrease in gait velocity that is greatest in adults with AD. Future research needs to investigate the effects of mobility aid training on gait performance.
Keywords: Aged; assistive devices; cane; dementia; gait.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosures available online (
Figures
References
-
- Wittwer JE, Webster KE, Menz HB (2010) A longitudinal study of measures of walking in people with Alzheimer’s disease. Gait Posture 32, 113–117. - PubMed
-
- Suttanon P, Hill KD, Said CM, Dodd KJ (2013) A longitudinal study of change in falls risk and balance and mobility in healthy older people and people with Alzheimer disease. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 92, 676–685. - PubMed
-
- Taylor ME, Delbaere K, Lord SR, Mikolaizak AS, Close JCT (2013) Physical impairments in cognitively impaired older people: Implications for risk of falls. Int Psychogeriatr 25, 148–56. - PubMed
-
- Tinetti ME, Speechley M, Ginter SF (1988) Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in the community. N Engl J Med 319, 1701–1707. - PubMed
-
- Asada T, Kariya T, Kinoshita T, Asaka A, Morikawa S, Yoshioka M, Kakuma T (1996) Predictors of fall-related injuries among community-dwelling elderly people with dementia. Age Ageing 25, 22–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

