Galectin-1 inhibition induces cell apoptosis through dual suppression of CXCR4 and Ras pathways in human malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors
- PMID: 31127849
- PMCID: PMC6827838
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/noz093
Galectin-1 inhibition induces cell apoptosis through dual suppression of CXCR4 and Ras pathways in human malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors
Abstract
Background: The Ras signaling pathway is commonly dysregulated in human malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs). It is well known that galectin-1 (Gal-1) is essential to stabilize membrane Ras and thereby induce the activation of Ras. However, the role of Gal-1 in MPNST progression remains unknown. The aim of this study was to examine whether Gal-1 knockdown could have an effect on the Ras signaling pathway.
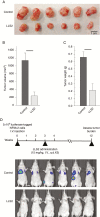
Methods: Cell viability, apoptosis assay, and colony formation were performed to examine the effects of inhibition of Gal-1 in MPNST cells. We used a human MPNST xenograft model to assess growth and metastasis inhibitory effects of Gal-1 inhibitor LLS2.
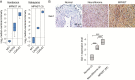
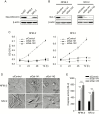
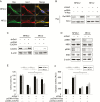
Results: Gal-1 was upregulated in MPNST patients and was highly expressed in MPNST cells. Knockdown of Gal-1 by small interfering (si)RNA in Gal-1 expressing MPNST cells significantly reduces cell proliferation through the suppression of C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) and the rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (RAS)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway, which are important oncogenic signaling in MPNST development. Moreover, Gal-1 knockdown induces apoptosis and inhibits colony formation. LLS2, a novel Gal-1 allosteric small molecule inhibitor, is cytotoxic against MPNST cells and was able to induce apoptosis and suppress colony formation in MPNST cells. LLS2 treatment and Gal-1 knockdown exhibited similar effects on the suppression of CXCR4 and RAS/ERK pathways. More importantly, inhibition of Gal-1 expression or function by treatment with either siRNA or LLS2 resulted in significant tumor responses in an MPNST xenograft model.
Conclusion: Our results identified an oncogenic role of Gal-1 in MPNST and that its inhibitor, LLS2, is a potential therapeutic agent, applied topically or systemically, against MPNST.
Keywords: CXCR4; LLS2; MPNST; RAS; galectin-1.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Comment in
-
Understanding a complicated Gal-1.Neuro Oncol. 2019 Nov 4;21(11):1341-1343. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noz165. Neuro Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31538650 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ferner RE. Neurofibromatosis 1. Eur J Hum Genet. 2007;15(2):131–138. - PubMed
-
- Van den Brûle FA, Waltregny D, Castronovo V. Increased expression of galectin-1 in carcinoma-associated stroma predicts poor outcome in prostate carcinoma patients. J. Pathol. 2001;193(1):80–87. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/1096-9896%282000%299999%... - PubMed
-
- Carlini MJ, Roitman P, Nuñez M, et al. . Clinical relevance of galectin-1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer. 2014;84(1):73–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

