Evaluation of the Dwell-Time and Dose Difference in Intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guèrin Therapy
- PMID: 31127897
- PMCID: PMC6857891
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.5.1389
Evaluation of the Dwell-Time and Dose Difference in Intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guèrin Therapy
Abstract
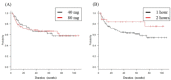
Objective: Bacillus Calmette-Guèrin (BCG) intravesical therapy is currently established using a low dose because of the high incidence of side-effects. Moreover, shortening the dwell time of BCG is conducted in some facilities owing to the complications associated with a long dwell time after injection. The method of BCG administration varies in each facility and even with each doctor. We evaluated whether the dwell-time and dose differences in patients who underwent intravesical BCG therapy is related to completion rates, adverse effects, and nonrecurrence rates. Methods: From November 2006 to April 2016, a total of 173 patients who received intravesical BCG therapy after transurethral resection of bladder tumor or transurethral biopsy were evaluated retrospectively. We allocated them into 4 groups based on the dose (40 or 80 mg BCG) and the dwell time (1 or 2 hours). Completion rate, side effects, and nonrecurrence rates were evaluated. Results: No significant improvement in the completion rate or reduction in side-effects was observed in any of the regimens. Although nonrecurrence rates for the 1-hour dwell time tended to be lower than the 2-hour dwell time, the difference was not significant. Conclusion: Our study suggests that reducing the BCG dose or shortening the dwell time does not reduce adverse effects or affect the nonrecurrence rate.
Keywords: BCG; dwell-time difference; dose difference.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sufficient prophylactic efficacy with minor adverse effects by intravesical instillation of low-dose bacillus Calmette-Guérin for superficial bladder cancer recurrence.Int J Urol. 2003 Apr;10(4):183-9. doi: 10.1046/j.0919-8172.2003.00607.x. Int J Urol. 2003. PMID: 12657096
-
Intravesical versus intravesical plus intradermal bacillus Calmette-Guerin: a prospective randomized study in patients with recurrent superficial bladder tumors.J Urol. 1996 Feb;155(2):483-7. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(01)66427-9. J Urol. 1996. PMID: 8558641 Clinical Trial.
-
[Long-term results and complications of intravesical instillation of bacillus Calmette-Guerin for prophylaxis of bladder cancer recurrence].Hinyokika Kiyo. 1994 Oct;40(10):873-7. Hinyokika Kiyo. 1994. PMID: 7992700 Clinical Trial. Japanese.
-
Intravesical Therapy for the Treatment of Nonmuscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Urol. 2017 May;197(5):1189-1199. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2016.12.090. Epub 2016 Dec 24. J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28027868
-
Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin treatment for Stage T1 grade 3 transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder.Urology. 1998 Nov;52(5):785-9. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(98)00369-0. Urology. 1998. PMID: 9801099 Review.
References
-
- Andius P, Fehrling M, Holmäng S. Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guèrin therapy:experience with a reduced dwell-time in patients with pronounced side-effects. BJU Int. 2005;96:1290–3. - PubMed
-
- Chang SS, Boorjian SA, Chou R, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer:AUA/SUO Guideline. J Urol. 2016;196:1021–9. - PubMed
-
- Drake MJ, Nixon PM, Crew JP. Drug-induced bladder and urinary disorders. Incidence, prevention and management. Drug Saf. 1998;19:45–55. - PubMed
-
- Lockyer CR, Sedgwick JE, Gillatt DA. Beware the BCG failures:a review of one institution's results. Eur Urol. 2002;42:542–6. - PubMed
-
- Martínez-Piñeiro JA, Flores N, Isorna S, et al. Long-term follow-up of a randomized prospective trial comparing a standard 81 mg dose of intravesical bacille Calmette-Guérin with a reduced dose of 27 mg in superficial bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2002;89:671–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

