Using Google Trends Data to Study Public Interest in Breast Cancer Screening in Malaysia
- PMID: 31127903
- PMCID: PMC6857874
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.5.1427
Using Google Trends Data to Study Public Interest in Breast Cancer Screening in Malaysia
Abstract
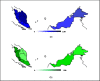
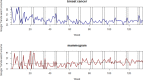
Objective: This study aims to investigate the public pattern in seeking breast cancer screening information in Malaysia using Google Trends. Methods: The Google Trends database was evaluated for the relative Internet search popularity of breast cancer and screening-related search terms from 2007 to 2018. Results: Result showed downward trends in breast cancer search, whereas mammogram and tomosynthesis search fluctuated consistently. A significant increment was found during Pink October month. Breast cancer search term achieved the highest popularity in the east coast of Malaysia with [x2 (5, N=661) = 110.93, P<0.05], whereas mammogram attained the highest search volume in central Malaysia [x2 (4, N=67) = 18.90, P<0.05]. The cross-correlation for breast cancer was moderate among northern Malaysia, Sabah, and Sarawak (0.3 ≤ rs ≤ 0.7). Conclusion: Public interest trend in breast cancer screening is strongly correlated with the breast cancer awareness campaign, Pink October. Breast cancer screening should be promoted in the rural areas in Malaysia.
Keywords: Breast cancer; mammogram; tomosynthesis; breast cancer screening; early detection of cancer.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures

Similar articles
-
Breast Cancer Screening Participation and Internet Search Activity in a Japanese Population: Decade-Long Time-Series Study.JMIR Cancer. 2025 Mar 4;11:e64020. doi: 10.2196/64020. JMIR Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40036529 Free PMC article.
-
The utility of Google Trends data to examine interest in cancer screening.BMJ Open. 2015 Jun 8;5(6):e006678. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-006678. BMJ Open. 2015. PMID: 26056120 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Public Interest in Mammography, Computed Tomography Lung Cancer Screening, and Computed Tomography Colonography Screening Examinations Using Internet Search Data: Cross-Sectional Study.JMIR Cancer. 2025 Mar 11;11:e53328. doi: 10.2196/53328. JMIR Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40068175 Free PMC article.
-
The uptake of Mammogram screening in Malaysia and its associated factors: A systematic review.Med J Malaysia. 2018 Aug;73(4):202-211. Med J Malaysia. 2018. PMID: 30121682
-
Digital breast tomosynthesis (3D-mammography) screening: A pictorial review of screen-detected cancers and false recalls attributed to tomosynthesis in prospective screening trials.Breast. 2016 Apr;26:119-34. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2016.01.007. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Breast. 2016. PMID: 27017251 Review.
Cited by
-
Interest in mammography across European countries: a retrospective "Google Trends" comparative study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Nov 1;13(11):7523-7529. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-196. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 37969630 Free PMC article.
-
Breast Cancer Screening Participation and Internet Search Activity in a Japanese Population: Decade-Long Time-Series Study.JMIR Cancer. 2025 Mar 4;11:e64020. doi: 10.2196/64020. JMIR Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40036529 Free PMC article.
-
Reddit and Google Activity Related to Non-COVID Epidemic Diseases Surged at Start of COVID-19 Pandemic: Retrospective Study.JMIR Form Res. 2023 Jul 6;7:e44603. doi: 10.2196/44603. JMIR Form Res. 2023. PMID: 37256832 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability of Google Trends: Analysis of the Limits and Potential of Web Infoveillance During COVID-19 Pandemic and for Future Research.Front Res Metr Anal. 2021 May 25;6:670226. doi: 10.3389/frma.2021.670226. eCollection 2021. Front Res Metr Anal. 2021. PMID: 34113751 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased Global Interest in Oral Cancer During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Jul 1;22(7):2117-2124. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.7.2117. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 34319034 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adeeb N, Nur-Azurah AG, Ong FB, et al. Utility of Pap Smears and mammograms in midlife Urban Malaysian women. Med Health. 2008;3:59–68.
-
- Ahadzadeh AS, Shari AP. Online health information seeking among Malaysia Women:Technology acceptace model perspective. Search. 2017;9:47–70.
-
- Al-Naggar RAM, Isa ZM, Shah SA, et al. Eight year survival among breast cancer Malaysian women from University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2009;10:1075–8. - PubMed
-
- Azizah AM, Nor Saleha IT, Noor Hashimah A, Asmah ZA, Mastulu W. Malaysian National Cancer Registry Report 2007-2011. Ministry of Health Malaysia. 2016
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

