PTEN modulates gene transcription by redistributing genome-wide RNA polymerase II occupancy
- PMID: 31127935
- PMCID: PMC6735678
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddz112
PTEN modulates gene transcription by redistributing genome-wide RNA polymerase II occupancy
Abstract
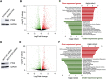
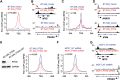
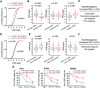
Control of gene expression is one of the most complex yet continuous physiological processes impacting cellular homeostasis. RNA polymerase II (Pol II) transcription is tightly regulated at promoter-proximal regions by intricate dynamic processes including Pol II pausing, release into elongation and premature termination. Pol II pausing is a phenomenon where Pol II complex pauses within 30-60 nucleotides after initiating the transcription. Negative elongation factor (NELF) and DRB sensitivity inducing factor (DSIF) contribute in the establishment of Pol II pausing, and positive transcription elongation factor b releases (P-TEFb) paused complex after phosphorylating DSIF that leads to dissociation of NELF. Pol II pausing is observed in most expressed genes across the metazoan. The precise role of Pol II pausing is not well understood; however, it's required for integration of signals for gene regulation. In the present study, we investigated the role of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) in genome-wide transcriptional regulation using PTEN overexpression and PTEN knock-down models. Here we identify that PTEN alters the expression of hundreds of genes, and its restoration establishes genome-wide Pol II promoter-proximal pausing in PTEN null cells. Furthermore, PTEN re-distributes Pol II occupancy across the genome and possibly impacts Pol II pause duration, release and elongation rate in order to enable precise gene regulation at the genome-wide scale. Our observations demonstrate an imperative role of PTEN in global transcriptional regulation that will provide a new direction to understand PTEN-associated pathologies and its management.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interactions between DSIF (DRB sensitivity inducing factor), NELF (negative elongation factor), and the Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription elongation complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 22;107(25):11301-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000681107. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20534440 Free PMC article.
-
Pause Patrol: Negative Elongation Factor's Role in Promoter-Proximal Pausing and Beyond.J Mol Biol. 2025 Jan 1;437(1):168779. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168779. Epub 2024 Sep 4. J Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39241983 Review.
-
Structure of paused transcription complex Pol II-DSIF-NELF.Nature. 2018 Aug;560(7720):601-606. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0442-2. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Nature. 2018. PMID: 30135580 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct negative elongation factor conformations regulate RNA polymerase II promoter-proximal pausing.Mol Cell. 2024 Apr 4;84(7):1243-1256.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.01.023. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38401543 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Promoter Proximal Pausing of RNA Polymerase II in Metazoans.J Mol Biol. 2021 Jul 9;433(14):166897. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166897. Epub 2021 Feb 25. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33640324 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PTEN interacts with RNA polymerase II to dephosphorylate polymerase II C-terminal domain.Oncotarget. 2019 Aug 13;10(48):4951-4959. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27128. eCollection 2019 Aug 13. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31452836 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN-negative endometrial cancer cells protect their genome through enhanced DDB2 expression associated with augmented nucleotide excision repair.BMC Cancer. 2023 May 4;23(1):399. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10892-5. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37142958 Free PMC article.
-
Germline PTEN mutations are associated with a skewed peripheral immune repertoire in humans and mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Aug 11;29(14):2353-2364. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa118. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 32588888 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN phosphatase inhibits metastasis by negatively regulating the Entpd5/IGF1R pathway through ATF6.iScience. 2023 Jan 26;26(2):106070. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106070. eCollection 2023 Feb 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 36824269 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in PTEN signalling axes in cancer.Fac Rev. 2020 Dec 23;9:31. doi: 10.12703/r/9-31. eCollection 2020. Fac Rev. 2020. PMID: 33659963 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liaw D., Marsh D.J., Li J., Dahia P.L., Wang S.I., Zheng Z., Bose S., Call K.M., Tsou H.C., Peacocke M. et al. (1997) Germline mutations of the PTEN gene in Cowden disease, an inherited breast and thyroid cancer syndrome. Nat. Genet., 16, 64–67. - PubMed
-
- Marsh D.J., Dahia P.L., Zheng Z., Liaw D., Parsons R., Gorlin R.J. and Eng C. (1997) Germline mutations in PTEN are present in Bannayan–Zonana syndrome. Nat. Genet., 16, 333–334. - PubMed
-
- Nieuwenhuis M.H., Kets C.M., Murphy-Ryan M., Yntema H.G., Evans D.G., Colas C., Moller P., Hes F.J., Hodgson S.V., Olderode-Berends M.J. et al. (2014) Cancer risk and genotype–phenotype correlations in PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome. Fam. Cancer, 13, 57–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

