A Novel lncRNA IHS Promotes Tumor Proliferation and Metastasis in HCC by Regulating the ERK- and AKT/GSK-3β-Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 31128422
- PMCID: PMC6535504
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.04.021
A Novel lncRNA IHS Promotes Tumor Proliferation and Metastasis in HCC by Regulating the ERK- and AKT/GSK-3β-Signaling Pathways
Abstract
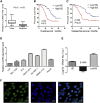
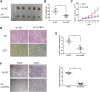
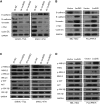
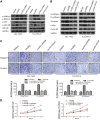
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in a variety of biological processes such as tumor proliferation and metastasis. A close relationship between hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) and SMYD3 in promoting the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was recently reported. However, the exact oncogenic mechanism of HBx-SMYD3 remains unknown. In this study, by performing lncRNA microarray analysis, we identified a novel lncRNA that was regulated by both HBx and SMYD3, and we named it lncIHS (lncRNA intersection between HBx microarray and SMYD3 microarray). lncIHS was overexpressed in HCC and decreased the survival rate of HCC patients. Knockdown of lncIHS inhibited HCC cell migration, invasion, and proliferation, and vice versa. Further study showed that lncIHS positively regulated the expression of epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related markers c-Myc and Cyclin D1, as well as the activation of the ERK- and AKT-signaling pathways. lncIHS exerted its oncogenic effect through ERK and AKT signaling. Moreover, results from transcriptome-sequencing analysis and mass spectrometry showed that lncIHS regulated multiple genes that were the upstream molecules of the ERK- and AKT-signaling pathways. Therefore, our findings suggest a regulatory network of ERK and AKT signaling through lncIHS, which is downstream of HBx-SMYD3, and they indicate that lncIHS may be a potential target for treating HCC.
Keywords: AKT; DUSP10; DUSP5; ERK; MAP3K8; SMYD3; hepatocellular carcinoma; lncRNA-HIS; metastasis; proliferation.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A Positive Feedback Loop of lncRNA HOXD-AS2 and SMYD3 Facilitates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression via the MEK/ERK Pathway.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023 Jul 27;10:1237-1256. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S416946. eCollection 2023. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023. PMID: 37533602 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus x protein induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating long non-coding RNA.Virol J. 2017 Dec 19;14(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0903-5. Virol J. 2017. PMID: 29258558 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx)-related long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) down-regulated expression by HBx (Dreh) inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by targeting the intermediate filament protein vimentin.Hepatology. 2013 May;57(5):1882-92. doi: 10.1002/hep.26195. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23239537
-
Long noncoding RNAs: Novel insights into hepatocelluar carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2014 Mar 1;344(1):20-27. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.10.021. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 24183851 Review.
-
SMYD3: An Oncogenic Driver Targeting Epigenetic Regulation and Signaling Pathways.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jan 6;12(1):142. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010142. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31935919 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A nuclear lncRNA Linc00839 as a Myc target to promote breast cancer chemoresistance via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Cancer Sci. 2020 Sep;111(9):3279-3291. doi: 10.1111/cas.14555. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 32619088 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA LINC00470 promotes proliferation through association with NF45/NF90 complex in hepatocellular carcinoma.Hum Cell. 2020 Jan;33(1):131-139. doi: 10.1007/s13577-019-00288-8. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Hum Cell. 2020. PMID: 31612313
-
MiR-199a-3p/5p participated in TGF-β and EGF induced EMT by targeting DUSP5/MAP3K11 in pterygium.J Transl Med. 2020 Sep 1;18(1):332. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02499-2. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32867783 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus x gene-downregulated growth-arrest specific 5 inhibits the cell viability and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines by activating Y-box-binding protein 1/p21 signaling.J Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Jun;16(2):179-190. doi: 10.1007/s12079-021-00645-z. Epub 2021 Sep 18. J Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 34535871 Free PMC article.
-
Biological functions and molecular mechanisms of LINC01116 in cancer.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 30;10(21):e38490. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38490. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39512466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Torre L.A., Bray F., Siegel R.L., Ferlay J., Lortet-Tieulent J., Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
- Torre, L.A., Bray, F., Siegel, R.L., Ferlay, J., Lortet-Tieulent, J., and Jemal, A. (2015). Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 65, 87-108. - PubMed
-
- Bellissimo F., Pinzone M.R., Cacopardo B., Nunnari G. Diagnostic and therapeutic management of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015;21:12003–12021. - PMC - PubMed
- Bellissimo, F., Pinzone, M.R., Cacopardo, B., and Nunnari, G. (2015). Diagnostic and therapeutic management of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 21, 12003-12021. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang L.Y., Fang F., Ou D.P., Wu W., Zeng Z.J., Wu F. Solitary large hepatocellular carcinoma: a specific subtype of hepatocellular carcinoma with good outcome after hepatic resection. Ann. Surg. 2009;249:118–123. - PubMed
- Yang, L.Y., Fang, F., Ou, D.P., Wu, W., Zeng, Z.J., and Wu, F. (2009). Solitary large hepatocellular carcinoma: a specific subtype of hepatocellular carcinoma with good outcome after hepatic resection. Ann. Surg. 249, 118-123. - PubMed
-
- Xia L., Huang W., Tian D., Zhu H., Qi X., Chen Z., Zhang Y., Hu H., Fan D., Nie Y., Wu K. Overexpression of forkhead box C1 promotes tumor metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2013;57:610–624. - PubMed
- Xia, L., Huang, W., Tian, D., Zhu, H., Qi, X., Chen, Z., Zhang, Y., Hu, H., Fan, D., Nie, Y., and Wu, K. (2013). Overexpression of forkhead box C1 promotes tumor metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 57, 610-624. - PubMed
-
- Ringelhan M., O’Connor T., Protzer U., Heikenwalder M. The direct and indirect roles of HBV in liver cancer: prospective markers for HCC screening and potential therapeutic targets. J. Pathol. 2015;235:355–367. - PubMed
- Ringelhan, M., O’Connor, T., Protzer, U., and Heikenwalder, M. (2015). The direct and indirect roles of HBV in liver cancer: prospective markers for HCC screening and potential therapeutic targets. J. Pathol. 235, 355-367. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

