A Regulator of Metabolic Reprogramming: MicroRNA Let-7
- PMID: 31128429
- PMCID: PMC6531867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2019.04.013
A Regulator of Metabolic Reprogramming: MicroRNA Let-7
Abstract
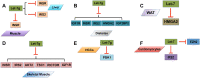
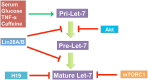
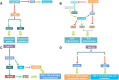
Let-7, a gene firstly known to control the timing of Caenorhabditis elegans larval development does not code for a protein but instead produces small non-coding RNAs, microRNAs. Higher animals have multiple isoforms of mature let-7 microRNAs. Mature let-7 family members share the same "seed sequence" and distinct from each other slightly by 'non-seed' sequence region. Let-7 has emerged as a central regulator of systemic energy homeostasis and it displays remarkable plasticity in metabolic responses to nutrients availability and physiological activities. In this review, we discuss recent studies highlighting post-transcriptional mechanisms that govern metabolic reprogramming in distinct cells by let-7. We focus on the participation of the let-7 clusters in immune cells, and suggest that tissue-specific regulation of the let-7 clusters by engineered mouse models might impact metabolic homeostasis and will be required to elucidate their physiological and pathological roles in the in vivo disease models.
Copyright © 2019 The Author. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biogenesis and regulation of the let-7 miRNAs and their functional implications.Protein Cell. 2016 Feb;7(2):100-13. doi: 10.1007/s13238-015-0212-y. Epub 2015 Sep 23. Protein Cell. 2016. PMID: 26399619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Doubletime Homolog KIN-20 Mainly Regulates let-7 Independently of Its Effects on the Period Homolog LIN-42 in Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2018 Jul 31;8(8):2617-2629. doi: 10.1534/g3.118.200392. G3 (Bethesda). 2018. PMID: 29880558 Free PMC article.
-
The time of appearance of the C. elegans let-7 microRNA is transcriptionally controlled utilizing a temporal regulatory element in its promoter.Dev Biol. 2003 Jul 15;259(2):364-79. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(03)00202-1. Dev Biol. 2003. PMID: 12871707
-
Functional relevance of "seed" and "non-seed" sequences in microRNA-mediated promotion of C. elegans developmental progression.RNA. 2015 Nov;21(11):1980-92. doi: 10.1261/rna.053793.115. Epub 2015 Sep 18. RNA. 2015. PMID: 26385508 Free PMC article.
-
The let-7 family of microRNAs.Trends Cell Biol. 2008 Oct;18(10):505-16. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.07.007. Epub 2008 Sep 4. Trends Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18774294 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-coding RNAs: The link between maternal malnutrition and offspring metabolism.Front Nutr. 2022 Nov 10;9:1022784. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1022784. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36438765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Neglected Insulin: IGF-II, a Metabolic Regulator with Implications for Diabetes, Obesity, and Cancer.Cells. 2019 Oct 6;8(10):1207. doi: 10.3390/cells8101207. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31590432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differentially Expressed MiRNAs of Goat Submandibular Glands Among Three Developmental Stages Are Involved in Immune Functions.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 15;12:678194. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.678194. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34211501 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles alleviate the immunometabolic dysfunction in murine septic encephalopathy.iScience. 2024 Jul 25;27(8):110573. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110573. eCollection 2024 Aug 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39165840 Free PMC article.
-
Ontogenetic Changes in the Expression of the Lin28 Protein in the Rat Hypothalamic Tuberal Nuclei.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 3;23(21):13468. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113468. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Neill L. Immunometabolism and the land of milk and honey. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17:217. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

