Effects of antiplatelet therapy after stroke due to intracerebral haemorrhage (RESTART): a randomised, open-label trial
- PMID: 31128924
- PMCID: PMC6617509
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30840-2
Effects of antiplatelet therapy after stroke due to intracerebral haemorrhage (RESTART): a randomised, open-label trial
Abstract
Background: Antiplatelet therapy reduces the risk of major vascular events for people with occlusive vascular disease, although it might increase the risk of intracranial haemorrhage. Patients surviving the commonest subtype of intracranial haemorrhage, intracerebral haemorrhage, are at risk of both haemorrhagic and occlusive vascular events, but whether antiplatelet therapy can be used safely is unclear. We aimed to estimate the relative and absolute effects of antiplatelet therapy on recurrent intracerebral haemorrhage and whether this risk might exceed any reduction of occlusive vascular events.
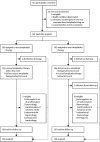
Methods: The REstart or STop Antithrombotics Randomised Trial (RESTART) was a prospective, randomised, open-label, blinded endpoint, parallel-group trial at 122 hospitals in the UK. We recruited adults (≥18 years) who were taking antithrombotic (antiplatelet or anticoagulant) therapy for the prevention of occlusive vascular disease when they developed intracerebral haemorrhage, discontinued antithrombotic therapy, and survived for 24 h. Computerised randomisation incorporating minimisation allocated participants (1:1) to start or avoid antiplatelet therapy. We followed participants for the primary outcome (recurrent symptomatic intracerebral haemorrhage) for up to 5 years. We analysed data from all randomised participants using Cox proportional hazards regression, adjusted for minimisation covariates. This trial is registered with ISRCTN (number ISRCTN71907627).
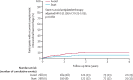
Findings: Between May 22, 2013, and May 31, 2018, 537 participants were recruited a median of 76 days (IQR 29-146) after intracerebral haemorrhage onset: 268 were assigned to start and 269 (one withdrew) to avoid antiplatelet therapy. Participants were followed for a median of 2·0 years (IQR [1·0- 3·0]; completeness 99·3%). 12 (4%) of 268 participants allocated to antiplatelet therapy had recurrence of intracerebral haemorrhage compared with 23 (9%) of 268 participants allocated to avoid antiplatelet therapy (adjusted hazard ratio 0·51 [95% CI 0·25-1·03]; p=0·060). 18 (7%) participants allocated to antiplatelet therapy experienced major haemorrhagic events compared with 25 (9%) participants allocated to avoid antiplatelet therapy (0·71 [0·39-1·30]; p=0·27), and 39 [15%] participants allocated to antiplatelet therapy had major occlusive vascular events compared with 38 [14%] allocated to avoid antiplatelet therapy (1·02 [0·65-1·60]; p=0·92).
Interpretation: These results exclude all but a very modest increase in the risk of recurrent intracerebral haemorrhage with antiplatelet therapy for patients on antithrombotic therapy for the prevention of occlusive vascular disease when they developed intracerebral haemorrhage. The risk of recurrent intracerebral haemorrhage is probably too small to exceed the established benefits of antiplatelet therapy for secondary prevention.
Funding: British Heart Foundation.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Restarting antiplatelet therapy after intracerebral haemorrhage.Lancet. 2019 Jun 29;393(10191):2567-2569. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31094-3. Epub 2019 May 22. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 31128927 No abstract available.
-
After stroke due to ICH while on antithrombotics, starting vs avoiding antiplatelets did not differ for symptomatic ICH.Ann Intern Med. 2019 Sep 17;171(6):JC32. doi: 10.7326/ACPJ201909170-032. Ann Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 31525766 No abstract available.
-
Effects of antiplatelet therapy after stroke due to intracerebral haemorrhage (RESTART): are neurologists feeling more comfortable to RESTART antiplatelet?Ann Transl Med. 2019 Sep;7(Suppl 6):S214. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.08.84. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31656793 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Safety and efficacy of restarting antiplatelet therapy after intracerebral hemorrhage.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Sep;7(Suppl 6):S218. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.08.96. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31656797 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Intracerebral haemorrhage on the acute stroke unit.J Neurol. 2020 Jan;267(1):295-297. doi: 10.1007/s00415-019-09663-9. J Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31820089 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Antiplatelet therapy after intracerebral haemorrhage.Natl Med J India. 2020 Jul-Aug;33(4):232-233. doi: 10.4103/0970-258X.316255. Natl Med J India. 2020. PMID: 34045378 No abstract available.
References
-
- Poon MT, Fonville AF, Al-Shahi Salman R. Long-term prognosis after intracerebral haemorrhage: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2014;85:660–667. - PubMed
- Poon MT, Fonville AF, Al-Shahi Salman R. Long-term prognosis after intracerebral haemorrhage: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2014; 85: 660–67. - PubMed
-
- Bejot Y, Cordonnier C, Durier J, Aboa-Eboule C, Rouaud O, Giroud M. Intracerebral haemorrhage profiles are changing: results from the Dijon population-based study. Brain. 2013;136:658–664. - PubMed
- Bejot Y, Cordonnier C, Durier J, Aboa-Eboule C, Rouaud O, Giroud M. Intracerebral haemorrhage profiles are changing: results from the Dijon population-based study. Brain 2013; 136: 658–64. - PubMed
-
- Pasquini M, Charidimou A, van Asch CJ. Variation in restarting antithrombotic drugs at hospital discharge after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2014;45:2643–2648. - PubMed
- Pasquini M, Charidimou A, van Asch CJ, et al. Variation in restarting antithrombotic drugs at hospital discharge after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2014; 45: 2643–48. - PubMed
-
- Antithrombotic Trialists' (ATT) Collaboration. Baigent C, Blackwell L. Aspirin in the primary and secondary prevention of vascular disease: collaborative meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised trials. Lancet. 2009;373:1849–1860. - PMC - PubMed
- Antithrombotic Trialists' (ATT) Collaboration, Baigent C, Blackwell L, et al. Aspirin in the primary and secondary prevention of vascular disease: collaborative meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised trials. Lancet 2009; 373: 1849–60. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hart RG, Pearce LA, Aguilar MI. Meta-analysis: antithrombotic therapy to prevent stroke in patients who have nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146:857–867. - PubMed
- Hart RG, Pearce LA, Aguilar MI. Meta-analysis: antithrombotic therapy to prevent stroke in patients who have nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Ann Intern Med 2007; 146: 857–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CH/1996001/9454/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G0400069/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SP/08/010/25939/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/14/50/30891/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- SP/14/3/31114/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MC_U137686849/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SCAF/17/01/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_U137686853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12026/6/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00017/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12026/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0300623/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1002605/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SP/12/2/29422/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

