Dextran-conjugated tetrathiatriarylmethyl radicals as biocompatible spin probes for EPR spectroscopy and imaging
- PMID: 31129052
- PMCID: PMC6557268
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.05.017
Dextran-conjugated tetrathiatriarylmethyl radicals as biocompatible spin probes for EPR spectroscopy and imaging
Abstract
Tetrathiatriarylmethyl (TAM) radicals represent soluble paramagnetic probes for biomedical electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR)-based spectroscopy and imaging. There is an increasing demand in the development of multifunctional, biocompatible and targeted trityl probes hampered by the difficulties in derivatization of the TAM structure. We proposed a new straightforward synthetic strategy using click chemistry for the covalent conjugation of the TAM radical with a water-soluble biocompatible carrier exemplified here by dextran. A set of dextran-grafted probes varied in the degrees of Finland trityl radical loading and dextran modification by polyethelene glycol has been synthesized. The EPR spectrum of the optimized macromolecular probe exhibits a single narrow line with high sensitivity to oxygen and has advantages over the unbound Finland trityl of being insensitive to interactions with albumin. In vivo EPR imaging of tissue oxygenation performed in breast tumor-bearing mouse using dextran-grafted probe demonstrates its utility for preclinical oximetric applications.
Keywords: Electron paramagnetic resonance; Spin probes; Trityl radicals.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
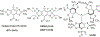





References
-
- Gomberg M, An instance of trivalent carbon: triphenylmethyl. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1900, 22, 757–771.
-
- Anderson S; Golman K; Rise F; Wikström H; Wistrand L-G, Free radicals. US Patent 1996, 5,530,140.
-
- Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH; Laursen I; Leunbach I; Ehnholm G; Wistrand LG; Petersson JS; Golman K, EPR and DNP properties of certain novel single electron contrast agents intended for oximetric imaging. J Magn Reson 1998, 133 (1), 1–12. - PubMed
-
- Krishna MC; English S; Yamada K; Yoo J; Murugesan R; Devasahayam N; Cook JA; Golman K; Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH; Subramanian S; Mitchell JB, Overhauser enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for tumor oximetry: coregistration of tumor anatomy and tissue oxygen concentration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002, 99 (4), 2216–21. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Epel B; Krzykawska-Serda M; Tormyshev V; Maggio MC; Barth ED; Pelizzari CA; Halpern HJ, Spin Lattice Relaxation EPR pO(2) Images May Direct the Location of Radiation Tumor Boosts to Enhance Tumor Cure. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics 2017, 75 (3–4), 295–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

