The escalating global burden of serious health-related suffering: projections to 2060 by world regions, age groups, and health conditions
- PMID: 31129125
- PMCID: PMC6560023
- DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30172-X
The escalating global burden of serious health-related suffering: projections to 2060 by world regions, age groups, and health conditions
Abstract
Background: Serious life-threatening and life-limiting illnesses place an enormous burden on society and health systems. Understanding how this burden will evolve in the future is essential to inform policies that alleviate suffering and prevent health system weakening. We aimed to project the global burden of serious health-related suffering requiring palliative care until 2060 by world regions, age groups, and health conditions.
Methods: We projected the future burden of serious health-related suffering as defined by the Lancet Commission on Palliative Care and Pain Relief, by combining WHO mortality projections (2016-60) with estimates of physical and psychological symptom prevalence in 20 conditions most often associated with symptoms requiring palliative care. Projections were described in terms of absolute numbers and proportional change compared with the 2016 baseline data. Results were stratified by World Bank income regions and WHO geographical regions.
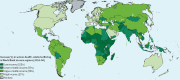
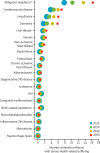
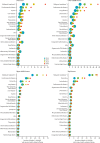
Findings: By 2060, an estimated 48 million people (47% of all deaths globally) will die with serious health-related suffering, which represents an 87% increase from 26 million people in 2016. 83% of these deaths will occur in low-income and middle-income countries. Serious health-related suffering will increase in all regions, with the largest proportional rise in low-income countries (155% increase between 2016 and 2060). Globally, serious health-related suffering will increase most rapidly among people aged 70 years or older (183% increase between 2016 and 2060). In absolute terms, it will be driven by rises in cancer deaths (16 million people, 109% increase between 2016 and 2060). The condition with the highest proportional increase in serious-related suffering will be dementia (6 million people, 264% increase between 2016 and 2060).
Interpretation: The burden of serious health-related suffering will almost double by 2060, with the fastest increases occurring in low-income countries, among older people, and people with dementia. Immediate global action to integrate palliative care into health systems is an ethical and economic imperative.
Funding: Research Challenge Fund, Florence Nightingale Faculty of Nursing, Midwifery and Palliative Care, King's College London.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Global palliative care: from need to action.Lancet Glob Health. 2019 Jul;7(7):e815-e816. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30223-2. Epub 2019 May 22. Lancet Glob Health. 2019. PMID: 31129121 No abstract available.
-
Palliative care: an essential facet of universal health coverage.Lancet Glob Health. 2019 Nov;7(11):e1488. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30323-7. Lancet Glob Health. 2019. PMID: 31607456 No abstract available.
-
Liberia's steps towards alleviating serious health-related suffering.Lancet Glob Health. 2019 Nov;7(11):e1489. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30332-8. Lancet Glob Health. 2019. PMID: 31607457 No abstract available.
References
-
- Knaul FM, Farmer PE, Krakauer EL. Alleviating the access abyss in palliative care and pain relief-imperative of universal health coverage: the Lancet Commission report. Lancet. 2018;391:1391–1454. - PubMed
- Knaul FM, Farmer PE, Krakauer EL, et al. Alleviating the access abyss in palliative care and pain relief-imperative of universal health coverage: the Lancet Commission report. Lancet 2018; 391: 1391–454. - PubMed
-
- WHO . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2014. Strengthening of palliative care as a component of comprehensive care throughout the life course.http://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/wha67/a67_r19-en.pdf - PubMed
- WHO. Strengthening of palliative care as a component of comprehensive care throughout the life course. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2014. http://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/wha67/a67_r19-en.pdf (accessed Dec 18, 2018).
-
- WHO . World Health Organization and The Worldwide Hospice Palliative Care Alliance; Geneva: 2014. The Worldwide Hospice Palliative Care Alliance. Global atlas of palliative care at the end of life.
- WHO. The Worldwide Hospice Palliative Care Alliance. Global atlas of palliative care at the end of life. Geneva: World Health Organization and The Worldwide Hospice Palliative Care Alliance, 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

