Blockade of the Sigma-1 Receptor Relieves Cognitive and Emotional Impairments Associated to Chronic Osteoarthritis Pain
- PMID: 31130863
- PMCID: PMC6510262
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00468
Blockade of the Sigma-1 Receptor Relieves Cognitive and Emotional Impairments Associated to Chronic Osteoarthritis Pain
Abstract
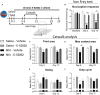
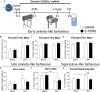
Osteoarthritis is the most common musculoskeletal disease worldwide, often characterized by degradation of the articular cartilage, chronic joint pain and disability. Cognitive dysfunction, anxiety and depression are common comorbidities that impact the quality of life of these patients. In this study, we evaluated the involvement of sigma-1 receptor (σ1R) on the nociceptive, cognitive and emotional alterations associated with chronic osteoarthritis pain. Monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) was injected into the knee of Swiss-albino CD1 mice to induce osteoarthritis pain, which then received a repeated treatment with the σ1R antagonist E-52862 or its vehicle. Nociceptive responses and motor performance were assessed with the von Frey and the Catwalk gait tests. Cognitive alterations were evaluated using the novel object recognition task, anxiety-like behavior with the elevated plus maze and the zero-maze tests, whereas depressive-like responses were determined using the forced swimming test. We also studied the local effect of the σ1R antagonist on cartilage degradation, and its central effects on microglial reactivity in the medial prefrontal cortex. MIA induced mechanical allodynia and gait abnormalities that were prevented by the chronic treatment with the σ1R antagonist. E-52862 also reduced the memory impairment and the depressive-like behavior associated to osteoarthritis pain. Interestingly, the effect of E-52862 on depressive-like behavior was not accompanied by a modification of anxiety-like behavior. The pain-relieving effects of the σ1R antagonist were not due to a local effect on the articular cartilage, since E-52862 treatment did not modify the histological alterations of the knee joints. However, E-52862 induced central effects revealed by a reduction of the cortical microgliosis observed in mice with osteoarthritis pain. These findings show that σ1R antagonism inhibits mechanical hypersensitivity, cognitive deficits and depressive-like states associated with osteoarthritis pain in mice. These effects are associated with central modulation of glial activity but are unrelated to changes in cartilage degradation. Therefore, targeting the σ1R with E-52862 represents a promising pharmacological approach with effects on multiple aspects of chronic osteoarthritis pain that may go beyond the strict inhibition of nociception.
Keywords: cognition; depression; medial prefrontal cortex; microglia; osteoarthritis; pain; sigma-1 receptor.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Involvement of the dynorphin/KOR system on the nociceptive, emotional and cognitive manifestations of joint pain in mice.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Apr;116:315-327. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.08.026. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 27567942
-
Monosodium iodoacetate-induced inflammation and joint pain are reduced in TRPA1 deficient mice--potential role of TRPA1 in osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015 Nov;23(11):2017-26. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2015.09.008. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015. PMID: 26521748
-
Supraspinal neuroinflammation and anxio-depressive-like behaviors in young- and older- adult mice with osteoarthritis pain: the effect of morphine.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2023 Oct;240(10):2131-2146. doi: 10.1007/s00213-023-06436-1. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2023. PMID: 37530884 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Modulation of the Sigma 1 Receptor and the Treatment of Pain.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;964:85-107. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50174-1_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28315267 Review.
-
Antinociception by Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonists: Central and Peripheral Effects.Adv Pharmacol. 2016;75:179-215. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2015.11.003. Epub 2016 Jan 27. Adv Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26920013 Review.
Cited by
-
Do eye diseases increase the risk of arthritis in the elderly population?Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jun 10;13(11):15580-15594. doi: 10.18632/aging.203122. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34111026 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonism of Sigma-1 receptor blocks heavy alcohol drinking and associated hyperalgesia in male mice.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021 Jul;45(7):1398-1407. doi: 10.1111/acer.14635. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 34060104 Free PMC article.
-
Rodent Animal Models of Endometriosis-Associated Pain: Unmet Needs and Resources Available for Improving Translational Research in Endometriosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 26;24(3):2422. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032422. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768741 Free PMC article.
-
Sigma-1 receptor modulates neuroinflammation associated with mechanical hypersensitivity and opioid tolerance in a mouse model of osteoarthritis pain.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Oct;176(20):3939-3955. doi: 10.1111/bph.14794. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31332781 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic nanocarriers as a therapeutic drug delivery strategy for promoting pain-related motor functions in a rat model of cartilage transplantation.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021 Mar 31;32(4):37. doi: 10.1007/s10856-021-06508-8. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021. PMID: 33787997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonini V., Marrazzo A., Kleiner G., Coradazzi M., Ronsisvalle S., Prezzavento O., et al. (2011). Anti-amnesic and neuroprotective actions of the sigma-1 receptor agonist (-)-MR22 in rats with selective cholinergic lesion and amyloid infusion. J. Alzheimers Dis. 24 569–586. 10.3233/JAD-2011-101794 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

