Supramolecular Complexes in Cell Death and Inflammation and Their Regulation by Autophagy
- PMID: 31131275
- PMCID: PMC6509160
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00073
Supramolecular Complexes in Cell Death and Inflammation and Their Regulation by Autophagy
Abstract
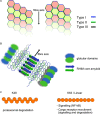
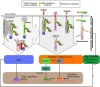
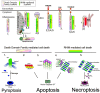
Signaling activation is a tightly regulated process involving myriad posttranslational modifications such as phosphorylation/dephosphorylation, ubiquitylation/deubiquitylation, proteolytical cleavage events as well as translocation of proteins to new compartments within the cell. In addition to each of these events potentially regulating individual proteins, the assembly of very large supramolecular complexes has emerged as a common theme in signal transduction and is now known to regulate many signaling events. This is particularly evident in pathways regulating both inflammation and cell death/survival. Regulation of the assembly and silencing of these complexes plays important roles in immune signaling and inflammation and the fate of cells to either die or survive. Here we will give a summary of some of the better studied supramolecular complexes involved in inflammation and cell death, particularly with a focus on diseases caused by their autoactivation and the role autophagy either plays or may be playing in their regulation.
Keywords: RHIM; autophagy; cargo receptors; cell death; death domain; inflammation; innate immunity; supramolecular complexes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Autophagy regulates inflammatory programmed cell death via turnover of RHIM-domain proteins.Elife. 2019 Jul 9;8:e44452. doi: 10.7554/eLife.44452. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31287416 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-Death or Pro-Survival: Contrasting Paradigms on Nanomaterial-Induced Autophagy and Exploitations for Cancer Therapy.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Nov 19;52(11):3164-3176. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00397. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31621285 Review.
-
Mechanisms and pathways of innate immune activation and regulation in health and cancer.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(11):3270-85. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.979640. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25625930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular architecture of signal complexes regulating immune cell function.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2008;(186):327-63. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-72843-6_14. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18491059 Review.
-
The Three Musketeers of Autophagy: phosphorylation, ubiquitylation and acetylation.Trends Cell Biol. 2011 Apr;21(4):195-201. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.12.006. Epub 2011 Jan 27. Trends Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21277210 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Myeloid autophagy genes protect mice against fatal TNF- and LPS-induced cytokine storm syndromes.Autophagy. 2023 Apr;19(4):1114-1127. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2116675. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 36056542 Free PMC article.
-
Nanocurcumin Modulates miR-223-3p and NF-κB Levels in the Pancreas of Rat Model of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome to Attenuate Autophagy Flare, Insulin Resistance and Improve ß Cell Mass.J Exp Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 26;13:873-888. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S323962. eCollection 2021. J Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34475786 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Omic Temporal Landscape of Plasma and Synovial Fluid-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Using an Experimental Model of Equine Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 4;24(19):14888. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914888. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834337 Free PMC article.
-
Osteogenesis imperfecta type 10 and the cellular scaffolds underlying common immunological diseases.Genes Immun. 2024 Aug;25(4):265-276. doi: 10.1038/s41435-024-00277-4. Epub 2024 May 29. Genes Immun. 2024. PMID: 38811682 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

