Low-Dose Imaging in a New Preclinical Total-Body PET/CT Scanner
- PMID: 31131277
- PMCID: PMC6509903
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00088
Low-Dose Imaging in a New Preclinical Total-Body PET/CT Scanner
Abstract
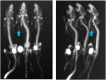
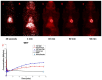
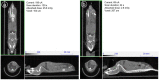
Ionizing radiation constitutes a health risk to imaging scientists and study animals. Both PET and CT produce ionizing radiation. CT doses in pre-clinical in vivo imaging typically range from 50 to 1,000 mGy and biological effects in mice at this dose range have been previously described. [18F]FDG body doses in mice have been estimated to be in the range of 100 mGy for [18F]FDG. Yearly, the average whole body doses due to handling of activity by PET technologists are reported to be 3-8 mSv. A preclinical PET/CT system is presented with design features which make it suitable for small animal low-dose imaging. The CT subsystem uses a X-source power that is optimized for small animal imaging. The system design incorporates a spatial beam shaper coupled with a highly sensitive flat-panel detector and very fast acquisition (<10 s) which allows for whole body scans with doses as low as 3 mGy. The mouse total-body PET subsystem uses a detector architecture based on continuous crystals, coupled to SiPM arrays and a readout based in rows and columns. The PET field of view is 150 mm axial and 80 mm transaxial. The high solid-angle coverage of the sample and the use of continuous crystals achieve a sensitivity of 9% (NEMA) that can be leveraged for use of low tracer doses and/or performing rapid scans. The low-dose imaging capabilities of the total-body PET subsystem were tested with NEMA phantoms, in tumor models, a mouse bone metabolism scan and a rat heart dynamic scan. The CT imaging capabilities were tested in mice and in a low contrast phantom. The PET low-dose phantom and animal experiments provide evidence that image quality suitable for preclinical PET studies is achieved. Furthermore, CT image contrast using low dose scan settings was suitable as a reference for PET scans. Total-body mouse PET/CT studies could be completed with total doses of <10 mGy.
Keywords: CT; PET; [18F]FDG; imaging; low dose; oncology; preclinical; total-body.
Figures





Similar articles
-
More advantages in detecting bone and soft tissue metastases from prostate cancer using 18F-PSMA PET/CT.Hell J Nucl Med. 2019 Jan-Apr;22(1):6-9. doi: 10.1967/s002449910952. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Hell J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30843003
-
Diagnostic reference levels for 18 F-FDG whole body PET/CT procedures: Results from a survey of 12 centres in Australia and New Zealand.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2019 Jun;63(3):291-299. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.12857. Epub 2019 Feb 15. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30770654
-
Application of the optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) technique for mouse dosimetry in micro-CT imaging.Med Phys. 2013 Dec;40(12):122102. doi: 10.1118/1.4829499. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 24320529
-
State of the art in total body PET.EJNMMI Phys. 2020 May 25;7(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40658-020-00290-2. EJNMMI Phys. 2020. PMID: 32451783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marriage of radiotracers and total-body PET/CT rapid imaging system: current status and clinical advances.Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023 Oct 20;13(5):195-207. eCollection 2023. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 38023815 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Multi-Scale and Multi-Technique Approach for the Characterization of the Effects of Spatially Fractionated X-ray Radiation Therapies in a Preclinical Model.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 1;13(19):4953. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194953. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638437 Free PMC article.
-
Biodistribution of andrographolide to assess the interior-exterior relationship between the lung and intestine using microPET.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Nov;11(11):3365-3374. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13682. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33017514 Free PMC article.
-
Light up heart-type fatty acid binding protein (FABP3) with a novel fluorine-18 labelled selective FABP3 ligand.EJNMMI Res. 2024 Nov 14;14(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13550-024-01175-6. EJNMMI Res. 2024. PMID: 39542944 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-low dose immunoPET using 64Cu-rituximab tracer for a human CD20 mouse model.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 7;12:1548132. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1548132. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40259986 Free PMC article.
-
Micro computed tomography analysis of barley during the first 24 hours of germination.Plant Methods. 2024 Sep 16;20(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s13007-024-01266-4. Plant Methods. 2024. PMID: 39285284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ionizing radiation, health effects and protective measures Key Facts. World Health Organization. (2016). Available online at: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ionizing-radiation-healt....
-
- McDougald WA, Collins R, Green M, Tavares AAS. High dose CT does not contribute toward improved MicroPET/CT image quantitative accuracy and can limit longitudinal scanning of small animals. Front Phys. (2017) 5:50 10.3389/fphy.2017.00050 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

