Melting Down Protein Stability: PAPS Synthase 2 in Patients and in a Cellular Environment
- PMID: 31131283
- PMCID: PMC6509946
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00031
Melting Down Protein Stability: PAPS Synthase 2 in Patients and in a Cellular Environment
Abstract
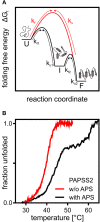
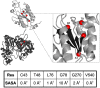
Within the crowded and complex environment of the cell, a protein experiences stabilizing excluded-volume effects and destabilizing quinary interactions with other proteins. Which of these prevail, needs to be determined on a case-by-case basis. PAPS synthases are dimeric and bifunctional enzymes, providing activated sulfate in the form of 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS) for sulfation reactions. The human PAPS synthases PAPSS1 and PAPSS2 differ significantly in their protein stability as PAPSS2 is a naturally fragile protein. PAPS synthases bind a series of nucleotide ligands and some of them markedly stabilize these proteins. PAPS synthases are of biomedical relevance as destabilizing point mutations give rise to several pathologies. Genetic defects in PAPSS2 have been linked to bone and cartilage malformations as well as a steroid sulfation defect. All this makes PAPS synthases ideal to study protein unfolding, ligand binding, and the stabilizing and destabilizing factors in their cellular environment. This review provides an overview on current concepts of protein folding and stability and links this with our current understanding of the different disease mechanisms of PAPSS2-related pathologies with perspectives for future research and application.
Keywords: PAPS synthase; enzyme storage complex; excluded volume effect; ligand stabilization; quinary interaction; sulfation pathways.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

