Identification of Genes Differentially Expressed in Simvastatin-Induced Alveolar Bone Formation
- PMID: 31131344
- PMCID: PMC6524672
- DOI: 10.1002/jbm4.10122
Identification of Genes Differentially Expressed in Simvastatin-Induced Alveolar Bone Formation
Abstract
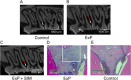
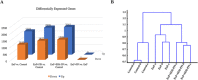
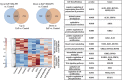
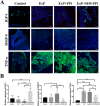
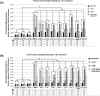
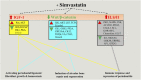
Local delivery of simvastatin (SIM) has exhibited potential in preventing inflammation and limiting bone loss associated with experimental periodontitis. The primary aim of this study was to analyze transcriptome changes that may contribute to SIM's reduction of periodontal inflammation and bone loss. We evaluate the global genetic profile and signaling mechanisms induced by SIM on experimental periodontitis bone loss and inflammation. Twenty mature female Sprague Dawley rats were subjected to ligature-induced experimental periodontitis around maxillary second molars (M2) either unilaterally (one side untreated, n = 10) or bilaterally (n = 10). After the ligature removal at day 7, sites were injected with either carrier, pyrophosphate (PPi ×3), 1.5-mg SIM-dose equivalent SIM-pyrophosphate prodrug, or no injection. Three days after ligature removal, animals were euthanized; the M1-M2 interproximal was evaluated with μCT, histology, and protein expression. M2 palatal gingiva was harvested for RNA sequencing. Although ligature alone caused upregulation of proinflammatory and bone catabolic genes and proteins, seen in human periodontitis, SIM-PPi upregulated anti-inflammatory (IL-10, IL-1 receptor-like 1) and bone anabolic (insulin-like growth factor, osteocrin, fibroblast growth factor, and Wnt/ β-catenin) genes. The PPi carrier alone did not have these effects. Genetic profile and signaling mechanism data may help identify enhanced pharmacotherapeutic approaches to limit or regenerate periodontitis bone loss. © 2018 The Authors. JBMR Plus Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Keywords: ANABOLICS; DENTAL BIOLOGY; GH/IGF‐1; MOLECULAR PATHWAYS–REMODELING; WNT/Β‐CATENIN/LRPS.
Figures
References
-
- Albandar J, Brunelle J, Kingman A. Destructive periodontal disease in adults 30 years of age and older in the United States, 1988–1994. J Periodontol. 1999; 70(1):13–29. - PubMed
-
- Eke PI, Dye BA, Wei L, Thornton‐Evans GO, Genco RJ. CDC Periodontal Disease Surveillance Workgroup: James Beck GDRP. Prevalence of periodontitis in adults in the United States: 2009 and 2010. J Dent Res. 2012; 91(10):914–20. - PubMed
-
- Eke PI, Dye B, Wei L, Thornton‐Evans G, Genco R. Prevalence of periodontitis in adults in the United States: 2009 and 2010. J Dent Res. 2012; 91(10):914–20. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann T, Al‐Machot E, Meyle J, Jervoe‐Storm PM, Jepsen S. Three‐year results following regenerative periodontal surgery of advanced intrabony defects with enamel matrix derivative alone or combined with a synthetic bone graft. Clin Oral Investig. 2016; 20 (2):357–64. - PubMed
-
- Pradeep AR, Priyanka N, Kalra N, Naik SB, Singh SP, Martande S. Clinical efficacy of subgingivally delivered 1.2‐mg simvastatin in the treatment of individuals with Class II furcation defects: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2012; 83 (12):1472–9. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
