Neoadjuvant treatment strategy for locally advanced thoracic esophageal cancer
- PMID: 31131355
- PMCID: PMC6524122
- DOI: 10.1002/ags3.12243
Neoadjuvant treatment strategy for locally advanced thoracic esophageal cancer
Abstract
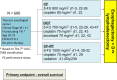
Multimodal treatment combining surgery with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy is necessary to improve the chances of survival in patients with locally advanced thoracic esophageal cancer. Based on the results of the Japan Clinical Oncology Group 9907 (JCOG9907) trial, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, two courses of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), followed by esophagectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy is the recommended treatment in Japan. Alternatively, neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (NACRT) typified by carboplatin and paclitaxel plus concurrent radiotherapy with 41.4 Gy (Chemoradiotherapy for Esophageal Cancer followed by Surgery Study [CROSS]) has shown promising outcomes in some Western countries. Currently, several clinical trials are being conducted within and outside of Japan to confirm the best neoadjuvant treatment regimen. For instance, a three-arm phase III randomized controlled trial (JCOG1109) is ongoing in Japan. The three arms comprise a doublet regimen (two courses of cisplatin 80 mg/m2 day 1 and 5-FU 800 mg/m2 days 1-5; repeated every 3 weeks) versus a triplet regimen (three courses of docetaxel, 70 mg/m2 day 1; cisplatin 70 mg/m2 day 1; and 5-FU 750 mg/m2 days 1-5; repeated every 3 weeks) versus a chemoradiotherapy (CRT) regimen (radiotherapy of 41.4 Gy/23 fractions with two courses of cisplatin 75 mg/m2 day 1 and 5-FU 1000 mg/m2 days 1-4; repeated every 4 weeks). Development of a multimodal strategy for neoadjuvant therapy is expected to receive the continuous focus of research in the hope of achieving better outcomes from treatment of patients with advanced thoracic esophageal cancer.
Keywords: esophagectomy; neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; perioperative chemotherapy; squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Y. Kitagawa received designated donation from Yakult Honsha Co., Ltd, Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd, Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, and ONO Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. His institution has endowed chairs of Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd and ONO Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Cancer Information Service NCC, Japan . Cancer Registry and Statistics. In. 2017.
-
- Japan Esophageal Society . Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Carcinoma of the Esophagus 2017. Tokyo: Kanehara 2017.
-
- Ando N, Kato H, Igaki H, et al. A randomized trial comparing postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with cisplatin and 5‐fluorouracil versus preoperative chemotherapy for localized advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus (JCOG9907). Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:68–74. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

