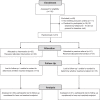
A Randomized Study of Passive versus Active PrEP Patient Navigation for a Heterogeneous Population at Risk for HIV in South Florida
- PMID: 31131679
- PMCID: PMC6748484
- DOI: 10.1177/2325958219848848
A Randomized Study of Passive versus Active PrEP Patient Navigation for a Heterogeneous Population at Risk for HIV in South Florida
Abstract
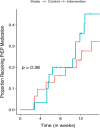
Effective approaches to promoting pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and linkage to PrEP care among those who may benefit the most from PrEP has proven to be a major challenge. We designed and pilot tested a strengths-based case management (SBCM) intervention for PrEP linkage. Adults interested in PrEP and meeting criteria (n = 61) were randomized to passive referral (control) or active SBCM (treatment). Outcomes measured were completion of provider visit, initiation of PrEP, and time to initiation of PrEP. Overall, 34% initiated PrEP by 12 weeks: 9 (29%) in the control group and 12 (40%) in the treatment group. The mean time to PrEP initiation was 13.1 weeks (95% confidence interval, 12.0-14.2) with no difference between groups ( P = .382). There was a 21% difference in achieving a provider visit between the treatment and control groups (53.3% versus 32.3%) by 12 weeks ( P = .096). Participants encountered financial, logistical, social, and provider-related barriers to PrEP access. Strengths-based case management-based patient navigation is a promising strategy for assisting PrEP seekers in obtaining a medical provider visit and initiating PrEP.
Keywords: HIV prevention; access to care; navigation; pre-exposure prophylaxis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Molina J-M, Capitant C, Spire B, et al. On demand PrEP with oral TDF-FTC in MSM: results of the ANRS Ipergay trial. In: Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections 2015.
-
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Diagnoses of HIV infection and AIDS in the United States and dependent areas, 2009. HIV Surveillance Report. 2011;21:1–79.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous