Hematopoietic-substrate-1 associated protein X-1 (HAX-1) regulates liver cancer cells growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis through Akt
- PMID: 31132019
- PMCID: PMC6741558
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2019.1617562
Hematopoietic-substrate-1 associated protein X-1 (HAX-1) regulates liver cancer cells growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis through Akt
Abstract
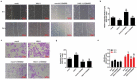
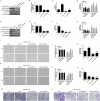
The aim of this study was to investigate the effects and mechanisms of hematopoietic-substrate-1-associated protein X-1 (HAX-1) on liver cancer cells. Information on HAX-1 from liver cancer patients was analyzed by the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) program. Cell migration and invasion abilities were respectively tested by scratch assay and transwell assay. Tube formation assay was applied to detect angiogenesis protein and mRNA was determined using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot. We found that the median month survival of HAX-1 overexpressing liver cancer patients was shorter than that of HAX-1 normal liver cancer patients. HAX-1 was overexpressed in liver cancer tissues and cells, and HAX-1 overexpression promoted the liver cancer cells growth, migration, and invasion, whereas silencing HAX-1 produced the opposite results. Inhibition of Akt by LY294002 reversed the migration and invasion abilities of liver cancer cells, and inhibited the ability of cells growth and angiogenesis. Silencing PIK3CA enhanced the inhibitory effects of HAX-1 silencing on the viability, migration, and invasion of liver cancer cells. HAX-1 affected liver cancer cells metastasis and angiogenesis by affecting Akt phosphorylation and FOXO3A expression.
Keywords: Akt; FOXO3A; Liver cancer; angiogenesis; hematopoietic-substrate-1 associated protein X-1.
Figures

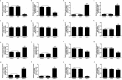
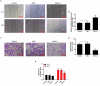
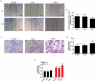


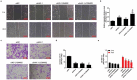

Similar articles
-
Effect of microRNA-135a on Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, Apoptosis and Tumor Angiogenesis Through the IGF-1/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(4):1431-1446. doi: 10.1159/000479207. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28715819
-
Hematopoietic Substrate-1-Associated Protein X-1 Regulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Endothelial Progenitor Cells Through Akt Pathway Modulation.Stem Cells. 2018 Mar;36(3):406-419. doi: 10.1002/stem.2741. Epub 2017 Nov 26. Stem Cells. 2018. PMID: 29139175
-
HAX-1 promotes the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the NF-κB pathway.Exp Cell Res. 2019 Aug 1;381(1):66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.04.030. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Exp Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31047882
-
Arsenic Trioxide Suppressed Migration and Angiogenesis by Targeting FOXO3a in Gastric Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 24;19(12):3739. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123739. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30477221 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol suppresses proliferation, migration, invasion, and tumor growth of liver cancer cells via suppressing cancer susceptibility candidate 9/phosphatase and tensin homolog/AKT serine/threonine kinase/mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase axis.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022 Jan-Dec;41:9603271211065972. doi: 10.1177/09603271211065972. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35238236
Cited by
-
HAX-1 overexpression in gastric cancer promotes cell proliferation.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Apr;9(4):2672-2682. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2020.02.69. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117626 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA‑125a‑5p regulates liver cancer cell growth, migration and invasion and EMT by targeting HAX1.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Nov;46(5):1849-1861. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4729. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33000203 Free PMC article.
-
QPCT regulation by CTCF leads to sunitinib resistance in renal cell carcinoma by promoting angiogenesis.Int J Oncol. 2021 Jul;59(1):48. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5228. Epub 2021 May 26. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34036385 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Integrin β6 and HAX-1 Correlates with Aggressive Features and Poor Prognosis in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Oct 2;12:9599-9608. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S274892. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 33061645 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-apoptotic HAX-1 suppresses cell apoptosis by promoting c-Abl kinase-involved ROS clearance.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Apr 4;13(4):298. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04748-2. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35379774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sugimachi K, Matsumura T, Hirata H, Uchi R, Ueda M, Ueo H, Shinden Y, Iguchi T, Eguchi H, Shirabe K, et al. Identification of a bona fide microRNA biomarker in serum exosomes that predicts hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after liver transplantation. Br J Cancer. 2015;112:532–538. doi:10.1038/bjc.2014.621. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Suzuki Y, Demoliere C, Kitamura D, Takeshita H, Deuschle U, Watanabe T. HAX-1, a novel intracellular protein, localized on mitochondria, directly associates with HS1, a substrate of Src family tyrosine kinases. J Immunol. 1997;158:2736–2744. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
