Antibiotic therapy for adults with neurosyphilis
- PMID: 31132142
- PMCID: PMC6536092
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011399.pub2
Antibiotic therapy for adults with neurosyphilis
Abstract
Background: Neurosyphilis is an infection of the central nervous system, caused by Treponema pallidum, a spirochete capable of infecting almost any organ or tissue in the body causing neurological complications due to the infection. This disease is a tertiary manifestation of syphilis. The first-line treatment for neurosyphilis is aqueous crystalline penicillin. However, in cases such as penicillin allergy, other regimes of antibiotic therapy can be used.
Objectives: To assess the clinical effectiveness and safety of antibiotic therapy for adults with neurosyphilis.
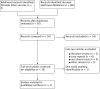
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Library, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, LILACS, World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform and Opengrey up to April 2019. We also searched proceedings of eight congresses to a maximum of 10 years, and we contacted trial authors for additional information.
Selection criteria: We included randomised clinical trials that included men and women, regardless of age, with definitive diagnoses of neurosyphilis, including HIV-seropositive patients. We compared any antibiotic regime (concentration, dose, frequency, duration), compared to any other antibiotic regime for the treatment for neurosyphilis in adults.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently selected eligible trials, extracted data, and evaluated risk of bias. We resolved disagreements by involving a third review author. For dichotomous data (serological cure, clinical cure, adverse events), we presented results as summary risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). We assessed the quality of evidence using the GRADE approach.
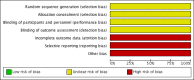
Main results: We identified one trial, with 36 participants diagnosed with syphilis and HIV. The participants were mainly men, with a median age of 34 years. This trial, funded by a pharmaceutical company, compared ceftriaxone in 18 participants (2 g daily for 10 days), with penicillin G, also in 18 participants (4 million/Units (MU)/intravenous (IV) every 4 hours for 10 days). The trial reported incomplete and inconclusive results. Three of 18 (16%) participants receiving ceftriaxone versus 2 of 18 (11%) receiving penicillin G achieved serological cure (RR 1.50; 95% CI: 0.28 to 7.93; 1 trial, 36 participants very low-quality evidence); and 8 of 18 (44%) participants receiving ceftriaxone versus 2 of 18 (18%) participants receiving penicillin G achieved clinical cure (RR 4.00; 95% CI: 0.98 to 16.30; 1 trial, 36 participants very low-quality evidence). Although more participants who received ceftriaxone achieved serological and clinical cure compared to those who received penicillin G, the evidence from this trial was insufficient to determine whether there was a difference between treatment with ceftriaxone or penicillin G.In this trial, the authors reported what would usually be adverse events as symptoms and signs in the follow-up of participants. Furthermore, this trial did not evaluate recurrence of neurosyphilis, time to recovery nor quality of life. We judged risk of bias in this clinical trial to be unclear for random sequence generation, allocation, and blinding of participants, and high for incomplete outcome data, potential conflicts of interest (funding bias), and other bias, due to the lack of a sample size calculation. We rated the quality of evidence as very low.
Authors' conclusions: Due to low quality and insufficient evidence, it was not possible to determine whether there was a difference between treatment with ceftriaxone or Penicillin G. Also, the benefits to people without HIV and neurosyphilis are unknown, as is the ceftriaxone safety profile.Therefore, these results should be interpreted with caution. This conclusion does not mean that antibiotics should not be used for treating this clinical entity. This Cochrane Review has identified the need of adequately powered trials, which should be planned according to Standard Protocol Items: Recommendations for Interventional Trials (SPIRIT) recommendations, conducted and reported as recommended by the CONSORT statement. Furthermore, the outcomes should be based on patients' perspectives taking into account Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) recommendations.
Conflict of interest statement
DB has no known conflicts of interest.
AMC has no known conflicts of interest.
AJ In 2016 and 2017 received payment for lectures from Procaps and Abbottt laboratories. This activity was not related to her work with The Cochrane Collaboration or any Cochrane Review.
LOC has no known conflicts of interest.
RP has no known conflicts of interest.
Figures




Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Marra 2000 {published data only}
-
- Marra CM, Boutin P, McArthur JC, Hurwitz S, Simpson PA, Haslett JA, et al. A pilot study evaluating ceftriaxone and penicillin G as treatment agents for neurosyphilis in human immunodeficiency virus‐infected individuals. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2000;30(3):540‐4. [PUBMED: 10722441] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Chesney 1949 {published data only}
-
- Chesney LP, Reynolds FW. Penicillin in treatment of neurosyphilis IV tabes dorsalis. British Journal of Venereal Diseases 1949;25:38.
Clement 2014 {published data only}
Dunaway 2017 {published data only}
-
- Dunaway S, Maxwell C, Tantalo L, Sahi S, Davis AP, Stevens C, et al. Treatment of neurosyphilis: IV penicillin G VS IM procaine penicillin/oral probenecid. Topics in Antiviral Medicine. 2017; Vol. 25, issue 1:319s.
Goldman 1950 {published data only}
-
- Goldman D. Neurosyphilis treated with penicillin. Report of 140 cases. British Journal of Venereal Diseases 1950;26:102. - PubMed
Hahn 1952 {published data only}
-
- Hahn RD, Lewis BI, Wiggal RH, Cross ES. The treatment of neurosyphilis with penicillin and with penicillin plus malaria. British Journal of Venereal Diseases 1952;28:41. - PubMed
Kopp 1949 {published data only}
-
- Kopp I, Rose AS, Solomon HC. The treatment of late symptomatic neurosyphilis at the Boston Psychopathic Hospital. A study of the results of penicillin therapy in 394 patients treated between February 1944 and March 1948. British Journal of Venereal Diseases 1949;25:213. - PubMed
Orban 1957 {published data only}
-
- Orbán T, Lazarovits L. Results of 5‐year old treatment of neurosyphilitics with penicillin. Wiener Medizinische Wochenschrift 1956;106(17):377‐81. - PubMed
-
- Orbán T, Lazarovits L. Results of five years of penicillin treatment of neurosyphilis. British Journal of Venereal Diseases 1957;33(1):59‐68.
Philcox 1987 {published data only}
-
- Philcox DV, Callanan JJ, Forder AA. Treatment of neurosyphilis. A comparison of penicillin regimens. South African Medical Journal 1987;72:110‐3. - PubMed
Potthoff 2009 {published data only}
-
- Potthoff A, Brockmeyer NH. Randomized, prospective, open‐label study to compare the efficacy of treatment with benzathine penicillin or ceftriaxone in early syphilis in HIV‐infected patients. HIV Medicine 2009;10:21.
Rolfs 1997 {published data only}
-
- Rolfs RT, Joesoef MR, Hendershot EF, Rompalo AM, Augenbraun MH, Chiu M, et al. A randomized trial of enhanced therapy for early syphilis in patients with and without human immunodeficiency virus infection. The Syphilis and HIV Study Group. New England Journal of Medicine 1997;337(5):307‐14. - PubMed
Short 1966 {published data only}
-
- Short DH, Knox JM, Glicksman J. Neurosyphilis, the search for adequate treatment. A review and report of a study using benzathine penicillin G. Archives of Dermatology 1966;93:87‐91. - PubMed
Smith 2004 {published data only}
-
- Smith NH, Musher DM, Huang DB, Rodriguez PS, Dowell ME, Ace W, et al. Response of HIV‐infected patients with asymptomatic syphilis to intensive intramuscular therapy with ceftriaxone or procaine penicillin. International Journal of STD & AIDS 2004;15:328‐32. - PubMed
Starzycki 1990 {published data only}
-
- Starzycki Z, Markiewicz J, Mayer J, Bogdaszewska‐Czabanowska J. Results of the treatment of neurosyphilis with high doses of crystalline and procaine penicillins. Przegla̧d Dermatologiczny 1990;77:359‐62. - PubMed
Tempski 1958 {published data only}
-
- Tempski J, Olszewska Z, Heykoporebski J. Evaluation of the treatment of neurosyphilis with penicillin and fever therapy. British Journal of Venereal Diseases 1958;34(1):60‐8.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Serragui 1999 {published data only}
-
- Serragui S, Yahyaoui M, Hassar M, Chkili T, Bouhaddioui N, Soulaymani R. A comparison study of two therapeutic protocols for neurosyphilis. Therapie 1999;54(5):613‐21. - PubMed
Additional references
Agwuh 2006
-
- Agwuh KN, MacGowan A. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the tetracyclines including glycylcyclines. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2006;58(2):256‐65. [PUBMED: 16816396] - PubMed
Ali 2002
-
- Ali L, Roos KL. Antibacterial therapy of neurosyphilis: lack of impact of new therapies. CNS Drugs 2002;16(12):799‐802. [PUBMED: 12421113] - PubMed
Ambrose 1984
-
- Ambrose PJ. Clinical pharmacokinetics of chloramphenicol and chloramphenicol succinate. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 1984;9(3):222‐38. [PUBMED: 6375931] - PubMed
Anonymous 2017
-
- Anonymous. Syphilis: an ancient disease in a modern era. Lancet 2017; Vol. 389, issue 10078:1492. [PUBMED: 28422012] - PubMed
Archer 2011
-
- Archer G, Polk RE. Chapter 133. Treatment and prophylaxis of bacterial infections. In: Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J editor(s). Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 18th Edition. New York: McGraw‐Hill Medical, 2011.
Belum 2013
-
- Belum GR, Belum VR, Chaitanya Arudra SK, Reddy BS. The Jarisch‐Herxheimer reaction: revisited. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease 2013;11(4):231‐7. [PUBMED: 23632012] - PubMed
Berger 2014
-
- Berger JR, Dean D. Neurosyphilis. Handbook of Clinical Neurology 2014;121:1461‐72. [PUBMED: 24365430] - PubMed
Bilgrami 2014
-
- Bilgrami M, O'Keefe P. Chapter 90: Neurologic diseases in HIV‐infected patients. In: Biller J, Ferro J editor(s). Neurologic Aspects of Systemic Disease Part III. Vol. 121, Elsevier, 2014:1321‐44. - PubMed
Brok 2009
-
- Brok J, Thorlund K, Wetterslev J, Gluud C. Apparently conclusive meta‐analyses may be inconclusive‐‐Trial sequential analysis adjustment of random error risk due to repetitive testing of accumulating data in apparently conclusive neonatal meta‐analyses. International journal of epidemiology 2009;38(1):287‐98. [PUBMED: 18824466] - PubMed
Brown 2003
-
- Brown DL, Frank JE. Diagnosis and management of syphilis. American Family Physician 2003;68(2):283‐90. [PUBMED: 12892348] - PubMed
CDC 2015
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines. www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/default.htm accessed (18 September 2018).
Chambers 2001
-
- Chambers HF. Protein synthesis inhibitors and miscellaneous antibacterial agents. In: Hardman JG, Limbird LE editor(s). Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10. New York: McGraw‐Hill Medical, 2001:1239‐71. [ISBN: 0‐07‐135469‐7]
Chen 2017
-
- Chen XS. Challenges in responses to syphilis epidemic. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2017;17(8):793‐4. [PUBMED: 28701274] - PubMed
Ciapponi 2011
-
- Ciapponi A, Glujovsky D, Bardach A, García Martí S, Comande D. EROS: a new software for early stage of systematic reviews. HTAi Conference, 8th annual meeting; 2011 June 27‐29; Rio de Janeiro. www.htai2011.org/documentos/HTAi_resumos_ISBN.pdf. Rio de Janeiro: Brazilian Ministry of Health, 2011.
Cohen 2013
-
- Cohen SE, Klausner JD, Engelman J, Philip S. Syphilis in the modern era: an update for physicians. Infectious Disease Clinics of North America 2013;27(4):705‐22. [PUBMED: 24275265] - PubMed
Conde‐Sendín 2002
-
- Cone‐Sendín MA, Hernández‐Fleta MA, Cárdenes‐Santana MA, Amela‐Peris R. Neurosyphilis forms of presentation and clinical management [Neurosífilis: formas de presentación y manejo]. Revista Neurología 2002;35(4):380‐6. - PubMed
CTU 2011 [Computer program]
-
- Copenhagen Trial Unit. Trial Sequential Analysis. Copenhagen: Copenhagen Trial Unit, 2011.
Daey 2014
-
- Daey Ouwens IM, Koedijk FD, Fiolet AT, Veen MG, Wijngaard KC, Verhoeven WM, et al. Neurosyphilis in the mixed urban‐rural community of the Netherlands. Acta Neuropsychiatrica 2014;26(3):186‐92. [PUBMED: 25142195] - PubMed
Deck 2012
-
- Deck DH, Winston LG. Chapter 44: Tetracyclines, macrolides, clindamycin, chloramphenicol, streptogramins, and oxazolidinones. In: Katzung BG, Masters SB, Trevor AJ editor(s). Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. 12. New York: McGraw‐Hill Medical, 2012.
Deeks 2017
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JP, Altman DG (editors) on behalf of the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017), Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Eisen 2010
-
- Eisen D. Doxycicline. In: Grayson LM, Crowe S, McCarthy JS, Mills J, Mouton JW, Norrby SR, et al. editor(s). Kucers' The Use of Antibiotics. 6th Edition. London, UK: Hodder Arnold, 2010:851‐69.
FDA 2012
-
- Food, Drug Administration. Determination that chloromycetin (chloramphenicol) capsules, 250 milligrams, were withdrawn from sale for reasons of safety or effectiveness. www.federalregister.gov/documents/2012/07/13/2012‐17091/determination‐th... 2012.
French 2009
-
- French P, Gomberg M, Janier M, Schmidt B, Voorst Vader P, Young H, IUSTI. IUSTI: 2008 European Guidelines on the management of syphilis. International Journal of STD & AIDS 2009;20(5):300‐9. - PubMed
Galvao 2013
Ghanem 2010
Glujovsky 2011
-
- Glujovsky D, Bardach A, García‐Martí S, Comandé D, Ciapponi A. PRM2 EROS: a new software for early stage of systematic reviews. Value in Health. Blackwell Science, 2011; Vol. 14, issue 7:A564.
GRADEpro GDT 2015 [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). GRADEpro GDT. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.
Guglielmo 2014
-
- Guglielmo B. Anti‐infective chemotherapeutic & antibiotic agents, chapter e1. In: Papadakis MA, McPhee SJ, Rabow MW editor(s). Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment. New York: McGraw‐Hill Medical, 2014.
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JP, Deeks JJ (editors). Chapter 7: Selecting studies and collecting data. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2017
-
- Higgins JP, Altman DG, Sterne JA (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017), Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Hook 2017
-
- Hook EW 3rd. Syphilis. Lancet 2017;389(10078):1550‐7. [PUBMED: 27993382] - PubMed
ICH‐GCP 1997
-
- ICH‐GCP. Expert Working Group International Conference on Harmonisation. Guideline for Good Clinical Practice. CFR & ICH Guidelines. Vol. 1, Pennsylvania: Barnett International ‐Parexel, 1997.
Jinno 2013
Katz 2012
Kent 2008
-
- Kent ME, Romanelli F. Reexamining syphilis: an update on epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2008;42(2):226‐36. [PUBMED: 18212261] - PubMed
Kingston 2008
-
- Kingston M, French P, Goh B, Goold P, Higgins S, Sukthankar A, et al. UK National Guidelines on the Management of Syphilis 2008. International Journal of STD & AIDS 2008;19(11):729‐40. [PUBMED: 18931264] - PubMed
Lagacé‐Wiens 2012
-
- Lagacé‐Wiens P, Rubinstein E. Adverse reactions to beta‐lactam antimicrobials. Expert Opinion on Drug Safety 2012;11(3):381‐99. [PUBMED: 22220627] - PubMed
Lasso 2009
-
- Lasso MB, Balcells ME, Fernández AS, Gaete PG, Serri MV, Pérez JG, et al. Neurosyphilis in the patients with and without HIV infection: description and comparison of two historical cohorts [Neurosífilis en pacientes portadores y no portadores de VIH: descripción y comparación de dos cohortes históricas]. Revista Chilena de Infectología 2009;26(6):540‐7. [20098789] - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org.
Levinson 2012
-
- Levinson WE. Chapter 10. Antimicrobial drugs: mechanism of action. Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology. Vol. 12th, New York: McGraw‐Hill Medical, 2012.
Macdougall 2011
Mahoney 1984
-
- Mahoney JF, Arnold RC, Sterner BL, Harris A, Zwall MR. Penicillin treatment of early syphilis: II. JAMA 1984;251(15):2005‐10. - PubMed
Marra 2004
-
- Marra CM, Maxwell CL, Smith SL, Lukehart SA, Rompalo AM, Eaton M, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid abnormalities in patients with syphilis: association with clinical and laboratory features. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2004;189(3):369‐76. [PUBMED: 14745693] - PubMed
Marra 2009
McQuay 1998
-
- McQuay HJ, Moore RA. An Evidence‐Based Resource for Pain Relief. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998.
Moher 2009
-
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta‐analyses: the PRISMA statement. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2009;62(10):1006‐12. [PUBMED: 19631508] - PubMed
Mohr 1976
-
- Mohr JA, Griffiths W, Jackson R, Saadah H, Bird P, Riddle J. Neurosyphilis and penicillin levels in cerebrospinal fluid. JAMA 1976;236(19):2208‐9. - PubMed
Musher 2008
-
- Musher DM. Neurosyphilis: diagnosis and response to treatment. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2008;47(7):900‐2. - PubMed
Nau 2010
Nayak 2012
Nguyen 2017
-
- Nguyen TL, Collins GS, Lamy A, Devereaux PJ, Daures JP, Landais P, et al. Simple randomization did not protect against bias in smaller trials. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2017;84:105‐13. [PUBMED: 28257927] - PubMed
O'Connor 2011
-
- O’Connor D, Green S, Higgins JP (editors). Chapter 5: Defining the review question and developing criteria for including studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org.
O'Donnell 2005
-
- O'Donnell JA, Emery CL. Neurosyphilis: a current review. Current Infectious Disease Reports 2005;7(4):277‐84. - PubMed
Philip 2014
-
- Philip S. Chapter 34. Spirochetal infections. In: Papadakis MA, McPhee SJ, Rabow MW editor(s). Current Medical Diagnosis and Treatment. New York: McGraw‐Hill Medical, 2014.
Pichichero 2007
-
- Pichichero ME, Casey JR. Safe use of selected cephalosporins in penicillin‐allergic patients: a meta‐analysis. Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery 2007;136(3):340‐7. [PUBMED: 17321857] - PubMed
Pietri 2001
-
- Petri WA Jr. Penicillins, cephalosporins, and other β‐lactam antibiotics. In: Hardman JG, Limbird LE editor(s). Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th Edition. New York: McGraw‐Hill Medical, 2001:1189‐1218. [ISBN: 0‐07‐135469‐7]
Porta 2014
-
- Porta M. A Dictionary of Epidemiology. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2014:79.
Ratnam 2005
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rowland 2010
-
- Rowland LP, Pedley TA, Merritt HH. Merritt's Neurology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2010.
Savovic 2012
-
- Savovic J, Jones H, Altman D, Harris R, Juni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomised controlled trials: combined analysis of meta‐epidemiological studies. Health Technology Assessment (Winchester, England) 2012;16(35):1‐82. [PUBMED: 22989478] - PubMed
Schünemann 2017
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Akl E, et al. on behalf of the Cochrane GRADEing Methods Group and the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Chapter 11: Completing ‘Summary of findings’ tables and grading the confidence in or quality of the evidence. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017). Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Stamm 2010
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta‐analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011;343:d4002. [PUBMED: 21784880] - PubMed
Thompson 1980
Timmermans 2004
Torres 2010
-
- Torres MJ, Blanca M. The complex clinical picture of beta‐lactam hypersensitivity: penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, carbapenems, and clavams. Medical Clinics of North America 2010;94(4):805‐20. [PUBMED: 20609864] - PubMed
Tramacere 2015
Unemo 2017
-
- Unemo M, Bradshaw CS, Hocking JS, Vries HJ, Francis SC, Mabey D, et al. Sexually transmitted infections: challenges ahead. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2017;17(8):e235‐e279. [PUBMED: 28701272] - PubMed
Van der Bij 2005
Wetterslev 2008
-
- Wetterslev J, Thorlund K, Brok J, Gluud C. Trial sequential analysis may establish when firm evidence is reached in cumulative meta‐analysis. Journal of clinical epidemiology 2008;61(1):64‐75. [PUBMED: 18083463] - PubMed
Yim 1985
Zetola 2007
-
- Zetola NM, Klausner JD. Syphilis and HIV infection: an update. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2007;44(9):1222‐8. [PUBMED: 17407043] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

