Emerging Role of Hepatobiliary Magnetic Resonance Contrast Media and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound for Noninvasive Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Emphasis on Recent Updates in Major Guidelines
- PMID: 31132813
- PMCID: PMC6536788
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0450
Emerging Role of Hepatobiliary Magnetic Resonance Contrast Media and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound for Noninvasive Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Emphasis on Recent Updates in Major Guidelines
Abstract
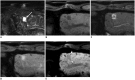
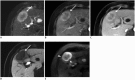
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) can be noninvasively diagnosed on the basis of its characteristic imaging findings of arterial phase enhancement and portal/delayed "washout" on computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in cirrhotic patients. However, different specific diagnostic criteria have been proposed by several countries and major academic societies. In 2018, major guideline updates were proposed by the Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), Korean Liver Cancer Association and National Cancer Center (KLCA-NCC) of Korea. In addition to dynamic CT and MRI using extracellular contrast media, these new guidelines now include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) using hepatobiliary contrast media as the first-line diagnostic test, while the KLCA-NCC and EASL guidelines also include contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) as the second-line diagnostic test. Therefore, hepatobiliary MR contrast media and CEUS will be increasingly used for the noninvasive diagnosis and staging of HCC. In this review, we discuss the emerging role of hepatobiliary phase MRI and CEUS for the diagnosis of HCC and also review the changes in the HCC diagnostic criteria in major guidelines, including the KLCA-NCC practice guidelines version 2018. In addition, we aimed to pay particular attention to some remaining issues in the noninvasive diagnosis of HCC.
Keywords: Criteria; Diagnosis; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Imaging techniques; Practice guidelines.
Copyright © 2019 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
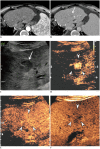
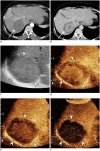
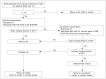
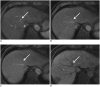
References
-
- Choo SP, Tan WL, Goh BKP, Tai WM, Zhu AX. Comparison of hepatocellular carcinoma in Eastern versus Western populations. Cancer. 2016;122:3430–3446. - PubMed
-
- Trevisani F, De Notariis S, Rapaccini G, Farinati F, Benvegnù L, Zoli M, et al. Semiannual and annual surveillance of cirrhotic patients for hepatocellular carcinoma: effects on cancer stage and patient survival (Italian experience) Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:734–744. - PubMed
-
- Ando E, Kuromatsu R, Tanaka M, Takada A, Fukushima N, Sumie S, et al. Surveillance program for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan: results of specialized department of liver disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;40:942–948. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

