Polymorphisms of Ionotropic Glutamate Receptor-Related Genes and the Risk of Autism Spectrum Disorder in a Chinese Population
- PMID: 31132842
- PMCID: PMC6539266
- DOI: 10.30773/pi.2019.02.26.3
Polymorphisms of Ionotropic Glutamate Receptor-Related Genes and the Risk of Autism Spectrum Disorder in a Chinese Population
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the association of GRIK2 and NLGN1 with autism spectrum disorder in a Chinese population.
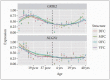
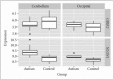
Methods: We performed spatio-temporal expression analysis of GRIK2 and NLGN1 in the developing prefrontal cortex, and examined the expression of the genes in ASD cases and healthy controls using the GSE38322 data set. Following, we performed a case-control study in a Chinese population.
Results: The analysis using the publicly available expression data showed that GRIK2 and NLGN1 may have a role in the development of human brain and contribute to the risk of ASD. Later genetic analysis in the Chinese population showed that the GRIK2 rs6922753 for the T allele, TC genotype and dominant model played a significant protective role in ASD susceptibility (respectively: OR=0.840, p=0.023; OR=0.802, p=0.038; OR=0.791, p=0.020). The NLGN1 rs9855544 for the G allele and GG genotype played a significant protective role in ASD susceptibility (respectively: OR=0.844, p=0.019; OR=0.717, p=0.022). After adjusting p values, the statistical significance was lost (p>0.05).
Conclusion: Our results suggested that GRIK2 rs6922753 and NLGN1 rs9855544 might not confer susceptibility to ASD in the Chinese population.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorder; GRIK2; Ionotropic glutamate receptors; NLGN1; Polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Meldrum BS. Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the brain: review of physiology and pathology. J Nutr. 2000;130(4S Suppl):1007S–1015S. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

