High sensitivity Troponin-I levels in asymptomatic hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 31132904
- PMCID: PMC6542185
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2019.1603110
High sensitivity Troponin-I levels in asymptomatic hemodialysis patients
Abstract
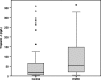
Reduction in renal clearance and removal by hemodialysis adversely affect the level and utility of high-sensitivity troponin I (hsTnI) for diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in hemodialysis (HD) patients. Furthermore, HD process itself might cause undesirable myocardial injury and enhance post HD hsTnI levels. This comparative cross-sectional study was conducted to compare the hsTnI levels between 100 asymptomatic HD patients and their 107 matched non-chronic kidney disease (CKD) population. The hsTnI levels in HD group were higher than non-CKD group [median (IQR): 54.3 (20.6-152.7) vs. 18 (6.2-66.1) ng/L, p < .001)]. The hsTnI levels reduced after HD process from 54.3 (20.6-152.7) ng/L in pre-HD to 27.1 (12.3-91.4) ng/L in post-HD (p = .015). Of interest, 25% of HD patients had increment of hsTnI after HD and might represent HD-induced myocardial injury. The significant risk factors were high hemoglobin level and high blood flow rate. In conclusion, the baseline hsTnI levels in asymptomatic HD patients were higher than non-CKD population. The dynamic change of hsTnI over time would be essential for the diagnosis of AMI. Certain numbers of asymptomatic HD patients had HD-induced silent myocardial injury and should be aggressively investigated to prevent further cardiovascular mortality.
Keywords: Hemodialysis; Troponin I; myocardial injury.
Figures
References
-
- Labugger R, Organ L, Collier C, et al. . Extensive troponin I and T modification detected in serum from patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2000;102:1221–1226. - PubMed
-
- Leszyk J, Dumaswala R, Potter JD, et al. . Amino acid sequence of bovine cardiac troponin I. Biochemistry. 1988;27:2821–2827. - PubMed
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD, et al. . Universal definition of myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2007;116:2634–2653. - PubMed
-
- Bonaca MP, Wiviott SD, Braunwald E, et al. . American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/European Society of Cardiology/World Heart Federation universal definition of myocardial infarction classification system and the risk of cardiovascular death: observations from the TRITON-TIMI 38 trial (Trial to Assess Improvement in Therapeutic Outcomes by Optimizing Platelet Inhibition With Prasugrel-Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction 38). Circulation. 2012;125:577–583. - PubMed
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. . Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2551–2567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous