Crystal structure of a cytocidal protein from lamprey and its mechanism of action in the selective killing of cancer cells
- PMID: 31133022
- PMCID: PMC6537362
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-019-0358-y
Crystal structure of a cytocidal protein from lamprey and its mechanism of action in the selective killing of cancer cells
Abstract
Background: In previous research, we found that lamprey immune protein (LIP) possessed cytocidal activity against tumor cells, but the mechanism of the selective recognition and killing of tumor cells by LIP was not identified.
Methods: Superresolution microscopy, crystallographic structural analysis, glycan chip assay, SPR experiments, FACS assays, computational studies and mass spectrometric analysis firmly establish the mode of action of LIP, which involves dual selective recognition and efficient binding.
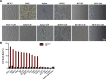
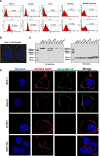
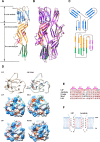
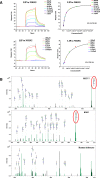
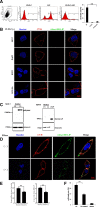
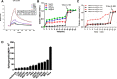
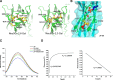
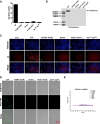
Results: We determined the overall crystallographic structure of LIP at a resolution of 2.25 Å. LIP exhibits an elongated structure with dimensions of 105 Å × 30 Å × 30 Å containing an N-terminal lectin module and a C-terminal aerolysin module. Moreover, the Phe209-Gly232 region is predicted to insert into the lipid bilayer to form a transmembrane β-barrel, in which the hydrophobic residues face the lipid bilayer, and the polar residues constitute the hydrophilic lumen of the pore. We found that LIP is able to kill various human cancer cells with minimal effects on normal cells. Notably, by coupling biochemical and computational studies, we propose a hypothetical mechanism that involves dual selective recognition and efficient binding dependent on both N-linked glycans on GPI-anchored proteins (GPI-APs) and sphingomyelin (SM) in lipid rafts. Furthermore, specific binding of the lectin module with biantennary bisialylated nonfucosylated N-glycan or sialyl Lewis X-containing glycan structures on GPI-APs triggers substantial conformational changes in the aerolysin module, which interacts with SM, ultimately resulting in the formation of a membrane-bound oligomer in lipid rafts.
Conclusions: LIP holds great potential for the application of a marine protein towards targeted cancer therapy and early diagnosis in humans.
Keywords: Cytotoxic activity; GPI-APs; LIP; Lamprey; Selective recognition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

