A GDF11/myostatin inhibitor, GDF11 propeptide-Fc, increases skeletal muscle mass and improves muscle strength in dystrophic mdx mice
- PMID: 31133057
- PMCID: PMC6537384
- DOI: 10.1186/s13395-019-0197-y
A GDF11/myostatin inhibitor, GDF11 propeptide-Fc, increases skeletal muscle mass and improves muscle strength in dystrophic mdx mice
Abstract
Background: Growth differentiation factor 11 (GDF11) is a member of the transforming growth factor β superfamily. The GDF11 propeptide, which is derived from the GDF11 precursor protein, blocks the activity of GDF11 and its homolog, myostatin, which are both potent inhibitors of muscle growth. Thus, treatment with GDF11 propeptide may be a potential therapeutic strategy for diseases associated with muscle atrophy like sarcopenia and the muscular dystrophies. Here, we evaluate the impact of GDF11 propeptide-Fc (GDF11PRO-Fc) gene delivery on skeletal muscle in normal and dystrophic adult mice.
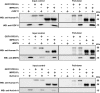
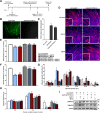
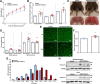
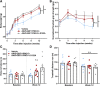
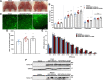
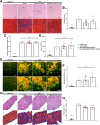
Methods: A pull-down assay was used to obtain physical confirmation of a protein-protein interaction between GDF11PRO-Fc and GDF11 or myostatin. Next, differentiated C2C12 myotubes were treated with AAV6-GDF11PRO-Fc and challenged with GDF11 or myostatin to determine if GDF11PRO-Fc could block GDF11/myostatin-induced myotube atrophy. Localized expression of GDF11PRO-Fc was evaluated via a unilateral intramuscular injection of AAV9-GDF11PRO-Fc into the hindlimb of C57BL/6J mice. In mdx mice, intravenous injection of AAV9-GDF11PRO-Fc was used to achieve systemic expression. The impact of GDF11PRO-Fc on muscle mass, function, and pathological features were assessed.
Results: GDF11PRO-Fc was observed to bind both GDF11 and myostatin. In C2C12 myotubes, expression of GDF11PRO-Fc was able to mitigate GDF11/myostatin-induced atrophy. Following intramuscular injection in C57BL/6J mice, increased grip strength and localized muscle hypertrophy were observed in the injected hindlimb after 10 weeks. In mdx mice, systemic expression of GDF11PRO-Fc resulted in skeletal muscle hypertrophy without a significant change in cardiac mass after 12 weeks. In addition, grip strength and rotarod latency time were improved. Intramuscular fibrosis was also reduced in treated mdx mice; however, there was no change seen in central nucleation, membrane permeability to serum IgG or serum creatine kinase levels.
Conclusions: GDF11PRO-Fc induces skeletal muscle hypertrophy and improvements in muscle strength via inhibition of GDF11/myostatin signaling. However, GDF11PRO-Fc does not significantly improve the dystrophic pathology in mdx mice.
Keywords: AAV; Duchenne muscular dystrophy; GDF11; Gene delivery; Gene therapy; Hypertrophy; Myostatin; mdx.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Harmon EB, et al. GDF11 modulates NGN3+ islet progenitor cell number and promotes beta-cell differentiation in pancreas development. Dev Camb Engl. 2004;131:6163–6174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

