snakePipes: facilitating flexible, scalable and integrative epigenomic analysis
- PMID: 31134269
- PMCID: PMC6853707
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz436
snakePipes: facilitating flexible, scalable and integrative epigenomic analysis
Abstract
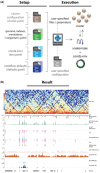
Summary: Due to the rapidly increasing scale and diversity of epigenomic data, modular and scalable analysis workflows are of wide interest. Here we present snakePipes, a workflow package for processing and downstream analysis of data from common epigenomic assays: ChIP-seq, RNA-seq, Bisulfite-seq, ATAC-seq, Hi-C and single-cell RNA-seq. snakePipes enables users to assemble variants of each workflow and to easily install and upgrade the underlying tools, via its simple command-line wrappers and yaml files.
Availability and implementation: snakePipes can be installed via conda: `conda install -c mpi-ie -c bioconda -c conda-forge snakePipes'. Source code (https://github.com/maxplanck-ie/snakepipes) and documentation (https://snakepipes.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) are available online.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Di Tommaso P. et al. (2017) Nextflow enables reproducible computational workflows. Nat. Biotechnol., 35, 316–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

