UNRAVEL: big data analytics research data platform to improve care of patients with cardiomyopathies using routine electronic health records and standardised biobanking
- PMID: 31134468
- PMCID: PMC6712144
- DOI: 10.1007/s12471-019-1288-4
UNRAVEL: big data analytics research data platform to improve care of patients with cardiomyopathies using routine electronic health records and standardised biobanking
Abstract
Introduction: Despite major advances in our understanding of genetic cardiomyopathies, they remain the leading cause of premature sudden cardiac death and end-stage heart failure in persons under the age of 60 years. Integrated research databases based on a large number of patients may provide a scaffold for future research. Using routine electronic health records and standardised biobanking, big data analysis on a larger number of patients and investigations are possible. In this article, we describe the UNRAVEL research data platform embedded in routine practice to facilitate research in genetic cardiomyopathies.
Design: Eligible participants with proven or suspected cardiac disease and their relatives are asked for permission to use their data and to draw blood for biobanking. Routinely collected clinical data are included in a research database by weekly extraction. A text-mining tool has been developed to enrich UNRAVEL with unstructured data in clinical notes.
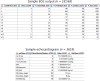
Preliminary results: Thus far, 828 individuals with a median age of 57 years have been included, 58% of whom are male. All data are captured in a temporal sequence amounting to a total of 18,565 electrocardiograms, 3619 echocardiograms, data from over 20,000 radiological examinations and 650,000 individual laboratory measurements.
Conclusion: Integration of routine electronic health care in a research data platform allows efficient data collection, including all investigations in chronological sequence. Trials embedded in the electronic health record are now possible, providing cost-effective ways to answer clinical questions. We explicitly welcome national and international collaboration and have provided our protocols and other materials on www.unravelrdp.nl .
Keywords: Big data analytics; Biobanking; Cardiomyopathy; Electronic health record; Machine learning; Research data platform.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Sammani, M. Jansen, M. Linschoten, A. Bagheri, N. de Jonge, H. Kirkels, L.W. van Laake, A. Vink, J.P. van Tintelen, D. Dooijes, A.S.J.M. te Riele, M. Harakalova, A. . Baas and F.W. Asselbergs declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Maron BJ, Towbin JA, Thiene G, et al. Contemporary definitions and classification of the cardiomyopathies: an American Heart Association Scientific Statement from the Council on Clinical Cardiology, Heart Failure and Transplantation Committee; Quality of Care and Outcomes Research and Functional Genomics and Translational Biology Interdisciplinary Working Groups; and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation. 2006;113:1807–1816. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.174287. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

