Protective effect of Echinacea purpurea (Immulant) against cisplatin-induced immunotoxicity in rats
- PMID: 31134491
- PMCID: PMC6593030
- DOI: 10.1007/s40199-019-00265-4
Protective effect of Echinacea purpurea (Immulant) against cisplatin-induced immunotoxicity in rats
Abstract
Purpose: Cisplatin, one of the most effective anticancer drugs, is known to cause undesirable adverse effects, including immunotoxicity. Echinacea purpurea is an important medicinal plant with immunostimulatory and anti-inflammatory activities. We have investigated the protective effect of an herbal formulation (Immulant) containing E. purpurea extract against cisplatin-induced immunotoxicity in rats.
Methods: Forty mature albino rats were randomized into four groups (10 rats/group). Control (group 1) animals were subjected to intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of saline solution (0.2 ml) once every 3 days. Group 2 animals received cisplatin (3.5 mg/kg, i.p.) once every 3 days for successive 2 weeks. Group 3 rats received oral Immulant (150 mg/kg) once daily for 2 weeks. Group 4 animals received oral Immulant treatment as in group 3 in addition to cisplatin as in group 2. Serum level of total protein and albumin, total and differential leukocytic count, phagocytic activity of monocytes, humoral activity and splenic histopathology and immunohistochemistry were used as diagnostic markers of immunotoxicity.
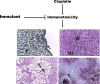
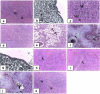
Results: Cisplatin induced marked inhibition of cellular immunity as exhibited by significant decrease of leukocytic count, lymphocyte percentage and phagocytic activity with marked increase in neutrophil percentage. Humoral immunity represented by marked inhibition in total protein and γ-globulin concentration and significant inhibition in antibody titer against Mycoplasma gallisepticum were recorded. Histopathological and immunohistochemical observation of the spleen of cisplatin-treated rats revealed obvious pathological findings of marked depletion and degeneration of lymphoid tissue. Co-oral administration of Immulant resulted in substantial improvement of various immunotoxicological indices compared to cisplatin control.
Conclusion: The herbal medicine Immulant is an immunostimulant which could be used to treat the immunotoxic effects of cisplatin. Graphical abstract Cisplatin (CP) is a highly effective antineoplastic DNA alkylating agent. CP induces free radical production causing an oxidative damage.Cisplatin induced marked inhibition in cellular and humoral immunityEchinacea purpurea (Immulant) is a powerful anticytotoxic agent against cisplatin toxicity.
Keywords: Cisplatin; Echinacea purpurea; Immulant; Immunotoxicity; Rats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oral administration of freshly expressed juice of Echinacea purpurea herbs fail to stimulate the nonspecific immune response in healthy young men: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study.J Immunother. 2002 Sep-Oct;25(5):413-20. doi: 10.1097/00002371-200209000-00005. J Immunother. 2002. PMID: 12218779 Clinical Trial.
-
Mast cell degranulation and calcium influx are inhibited by an Echinacea purpurea extract and the alkylamide dodeca-2E,4E-dienoic acid isobutylamide.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Feb 15;212:166-174. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.10.012. Epub 2017 Oct 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29042288 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of Echinacea purpurea on the pharmacokinetics of docetaxel.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;76(3):467-74. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12159. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23701184 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Applications of the phytomedicine Echinacea purpurea (Purple Coneflower) in infectious diseases.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:769896. doi: 10.1155/2012/769896. Epub 2011 Oct 26. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22131823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echinacea species (Echinacea angustifolia (DC.) Hell., Echinacea pallida (Nutt.) Nutt.,Echinacea purpurea (L.) Moench): a review of their chemistry, pharmacology and clinical properties.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2005 Aug;57(8):929-54. doi: 10.1211/0022357056127. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16102249 Review.
Cited by
-
Nutraceuticals as Modulators of Immune Function: A Review of Potential Therapeutic Effects.Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2023 Jun 30;28(2):89-107. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2023.28.2.89. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2023. PMID: 37416796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer Activity of Metallodrugs and Metallizing Host Defense Peptides-Current Developments in Structure-Activity Relationship.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 3;25(13):7314. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137314. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echinacea purpurea (L.) Moench: Biological and Pharmacological Properties. A Review.Plants (Basel). 2022 May 5;11(9):1244. doi: 10.3390/plants11091244. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35567246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effect of Polysaccharides Extracted from Cudrania tricuspidata Fruit against Cisplatin-Induced Cytotoxicity in Macrophages and a Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 13;22(14):7512. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147512. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299130 Free PMC article.
-
Common contributing factors to COVID-19 and inflammatory bowel disease.Toxicol Rep. 2021;8:1616-1637. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.08.007. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Toxicol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34485092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hasaaan I, Chibber S, Naseem I. Ameliorative effect of riboflavin on the cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity under photoillumination. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010;48:2050–2058. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

