Angular Electrode Insertion Depth and Speech Perception in Adults With a Cochlear Implant: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 31135680
- PMCID: PMC6641467
- DOI: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002298
Angular Electrode Insertion Depth and Speech Perception in Adults With a Cochlear Implant: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Objective: By discussing the design, findings, strengths, and weaknesses of available studies investigating the influence of angular insertion depth on speech perception, we intend to summarize the current status of evidence; and using evidence based conclusions, possibly contribute to the determination of the optimal cochlear implant (CI) electrode position.
Data sources: Our search strategy yielded 10,877 papers. PubMed, Ovid EMBASE, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library were searched up to June 1, 2018. Both keywords and free-text terms, related to patient population, predictive factor, and outcome measurements were used. There were no restrictions in languages or year of publication.
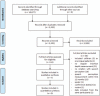
Study selection: Seven articles were included in this systematic review. Articles eligible for inclusion: (a) investigated cochlear implantation of any CI system in adults with post-lingual onset of deafness and normal cochlear anatomy; (b) investigated the relationship between angular insertion depth and speech perception; (c) measured angular insertion depth on imaging; and (d) measured speech perception at, or beyond 1-year post-activation.
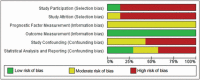
Data extraction and synthesis: In included studies; quality was judged low-to-moderate and risk of bias, evaluated using a Quality-in-Prognostic-Studies-tool (QUIPS), was high. Included studies were too heterogeneous to perform meta-analyses, therefore, effect estimates of the individual studies are presented. Six out of seven included studies found no effect of angular insertion depth on speech perception.
Conclusion: All included studies are characterized by methodological flaws, and therefore, evidence-based conclusions regarding the influence of angular insertion depth cannot be drawn to date.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have a personal conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Baskent D, Shannon RV. Interactions between cochlear implant electrode insertion depth and frequency-place mapping. J Acoust Soc Am 2005; 117 (3 pt 1):1405–1416. - PubMed
-
- Faulkner A, Rosen S, Norman C. The right information may matter more than frequency-place alignment: simulations of frequency-aligned and upward shifting cochlear implant processors for a shallow electrode array insertion. Ear Hear 2006; 27:139–152. - PubMed
-
- Suhling MC, Ketten DR, Salcher R, et al. The impact of electrode array length on hearing preservation in cochlear implantation. Otol Neurotol 2016; 37:1006–1015. - PubMed
-
- Causon A, Verschuur C, Newman TA. A retrospective analysis of the contribution of reported factors in cochlear implantation on hearing preservation outcomes. Otol Neurotol 2015; 36:1137–1145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

