Diffusion-Weighted MRI of Breast Cancer: Improved Lesion Visibility and Image Quality Using Synthetic b-Values
- PMID: 31136044
- PMCID: PMC6899592
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.26809
Diffusion-Weighted MRI of Breast Cancer: Improved Lesion Visibility and Image Quality Using Synthetic b-Values
Abstract
Background: Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is an MRI technique with the potential to serve as an unenhanced breast cancer detection tool. Synthetic b-values produce images with high diffusion weighting to suppress residual background signal, while avoiding additional measurement times and reducing artifacts.
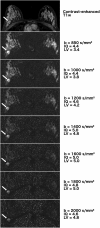
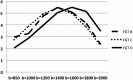
Purpose: To compare acquired DWI images (at b = 850 s/mm2 ) and different synthetic b-values (at b = 1000-2000 s/mm2 ) in terms of lesion visibility, image quality, and tumor-to-tissue contrast in patients with malignant breast tumors.
Study type: Retrospective.
Population: Fifty-three females with malignant breast lesions.
Field strength/sequence: T2 w, DWI EPI with STIR fat-suppression, and dynamic contrast-enhanced T1 w at 3T.
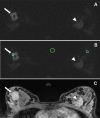
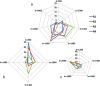
Assessment: From acquired images using b-values of 50 and 850 s/mm2 , synthetic images were calculated at b = 1000, 1200, 1400, 1600, 1800, and 2000 s/mm2 . Four readers independently rated image quality, lesion visibility, preferred b-value, as well as the lowest and highest b-value, over the range of b-values tested, to provide a diagnostic image.
Statistical tests: Medians and mean ranks were calculated and compared using the Friedman test and Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Reproducibility was analyzed by intraclass correlation (ICC), Fleiss, and Cohen's κ.
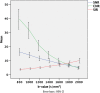
Results: Relative signal-to-noise and contrast-to-noise ratios decreased with increasing b-values, while the signal-intensity ratio between tumor and tissue increased significantly (P < 0.001). Intermediate b-values (1200-1800 s/mm2 ) were rated best concerning image quality and lesion visibility; the preferred b-value mostly lay at 1200-1600 s/mm2 . Lowest and highest acceptable b-values were 850 s/mm2 and 2000 s/mm2 . Interreader agreement was moderate to high concerning image quality (ICC: 0.50-0.67) and lesion visibility (0.70-0.93), but poor concerning preferred and acceptable b-values (κ = 0.032-0.446).
Data conclusion: Synthetically increased b-values may be a way to improve tumor-to-tissue contrast, lesion visibility, and image quality of breast DWI, while avoiding the disadvantages of performing DWI at very high b-values.
Level of evidence: 3 Technical Efficacy: Stage 2 J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019;50:1754-1761.
Keywords: Breast neoplasms; computer-assisted image processing; diffusion magnetic resonance imaging; magnetic resonance imaging.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures

References
-
- Monticciolo DL, Newell MS, Moy L, Niell B, Monsees B, Sickles EA. Breast cancer screening in women at higher‐than‐average risk: Recommendations from the ACR. J Am Coll Radiol 2018;15(3 Pt A):408–414. - PubMed
-
- Sardanelli F, Boetes C, Borisch B, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the breast: Recommendations from the EUSOMA working group. Eur J Cancer 2010;46:1296–1316. - PubMed
-
- Saslow D, Boetes C, Burke W, et al. American Cancer Society guidelines for breast screening with MRI as an adjunct to mammography. CA Cancer J Clin 2007;57:75–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

