Correlation of tools for objective evaluation of infravesical obstruction of men with lower urinary tract symptoms
- PMID: 31136110
- PMCID: PMC6837608
- DOI: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2018.0706
Correlation of tools for objective evaluation of infravesical obstruction of men with lower urinary tract symptoms
Abstract
Purpose: To identify how the most frequently used parameters in daily clinical practice diagnosing bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) due to benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) correlate to each other.
Materials and methods: The study included 452 patients with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) of the UNICAMP urology outpatient clinic of LUTS.
Inclusion criteria: patients with BOO due to BPH who agreed to participate in the study.
Exclusion criteria: patients with urinary tract infection, neurological diseases that compromised the lower urinary tract, prior prostatic surgery, radiotherapy or urethral stenosis. Patient assessment: history, international prostate symptoms score (IPSS), nocturnal quality of life score (NQoL) questionnaires, physical and digital rectal examination (DRE), PSA, transabdominal ultrasound with intravesical prostate protrusion (IPP), post-mictional residue and free urofl owmetry.
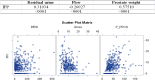
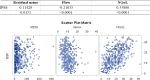
Results: There was no strong Spearman correlation among the studied variables. The only moderate correlations occurred between IPSS and NQoL (p<0001; c=0.56) and between IPP and prostate volume (p<0001; c=0.57). Weak correlations between IPP and post-mictional residue (p<0001; c=0.31) and free urofl owmetry (p<0001; c=-0.26); and between IPSS and free urofl owmetry (p<0001, c=-0.21) were observed.
Conclusion: In this study, we found moderate, weak, very weak and absent correlation among the various parameters used in the diagnosis and management of BOO due to BPH. As the value of these tools is variable, the creation of a logical and objective algorithm was not possible and the treatment is based on the interpretation of clinical symptoms.
Keywords: Prostate; Prostatic Hyperplasia; Transurethral Resection of Prostate.
Copyright® by the International Brazilian Journal of Urology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of resistive index of the prostate and bladder sonomorphologic parameters as replacements for urodynamics to predict bladder outlet obstruction in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia.Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2019 May;11(3):163-168. doi: 10.1111/luts.12256. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2019. PMID: 30793849
-
[Correlation of serum prostate specific antigen, the volume and the intravesical prostatic protrusion for diagnosing bladder outlet obstruction in patients with benign prostate hyperplasia].Hell J Nucl Med. 2007 May-Aug;10(2):138-43. Hell J Nucl Med. 2007. PMID: 17684595 Greek, Modern.
-
Videourodynamic findings of lower urinary tract dysfunctions in men with persistent storage lower urinary tract symptoms after medical treatment.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 20;13(2):e0190704. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190704. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29462145 Free PMC article.
-
EAU Guidelines on the Assessment of Non-neurogenic Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms including Benign Prostatic Obstruction.Eur Urol. 2015 Jun;67(6):1099-1109. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.12.038. Epub 2015 Jan 19. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 25613154 Review.
-
[Clinical impact of the intravesical prostatic protrusion: a review by the LUTS committee of the French Urological Association].Prog Urol. 2014 Apr;24(5):313-8. doi: 10.1016/j.purol.2013.09.009. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Prog Urol. 2014. PMID: 24674338 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Clinical analysis of transurethral holmium laser enucleation in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with prostatic inflammation: A prospective research study.Front Surg. 2023 Jan 6;9:1026657. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1026657. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 36684154 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between interviewer-assisted international prostate symptom score and other objective measures of bladder outlet obstruction in Southeast Nigeria: a cross-sectional study.Pan Afr Med J. 2023 Nov 21;46:87. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2023.46.87.37303. eCollection 2023. Pan Afr Med J. 2023. PMID: 38314235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 1. Parsons JK. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Epidemiology and Risk Factors. Curr Bladder Dysfunct Rep. 2010;5:212-8. - PMC - PubMed
- Parsons JK. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Epidemiology and Risk Factors. Curr Bladder Dysfunct Rep. 2010;5:212–218. - PMC - PubMed
-
- 2. Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn. 2002;21:167-78. - PubMed
- Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn. 2002;21:167–178. - PubMed
-
- 3. Barry MJ, Fowler FJ Jr, O’Leary MP, Bruskewitz RC, Holtgrewe HL, Mebust WK, et al. The American Urological Association symptom index for benign prostatic hyperplasia. The Measurement Committee of the American Urological Association. J Urol. 1992;148:1549-57. - PubMed
- Barry MJ, Fowler FJ, Jr, O’Leary MP, Bruskewitz RC, Holtgrewe HL, Mebust WK, et al. The American Urological Association symptom index for benign prostatic hyperplasia. The Measurement Committee of the American Urological Association. J Urol. 1992;148:1549–1557. - PubMed
-
- 4. Roehrborn CG, McConnell J, Bonilla J, Rosenblatt S, Hudson PB, Malek GH, et al. Serum prostate specific antigen is a strong predictor of future prostate growth in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. PROSCAR long-term efficacy and safety study. J Urol. 2000;163:13-20. - PubMed
- Roehrborn CG, McConnell J, Bonilla J, Rosenblatt S, Hudson PB, Malek GH, et al. Serum prostate specific antigen is a strong predictor of future prostate growth in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. PROSCAR long-term efficacy and safety study. J Urol. 2000;163:13–20. - PubMed
-
- 5. Abraham L, Hareendran A, Mills IW, Martin ML, Abrams P, Drake MJ, et al. Development and validation of a quality-of-life measure for men with nocturia. Urology. 2004;63:481-6. - PubMed
- Abraham L, Hareendran A, Mills IW, Martin ML, Abrams P, Drake MJ, et al. Development and validation of a quality-of-life measure for men with nocturia. Urology. 2004;63:481–486. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous