Chemopreventive efficacy of oral curcumin: a prodrug hypothesis
- PMID: 31136203
- PMCID: PMC9272759
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201900166R
Chemopreventive efficacy of oral curcumin: a prodrug hypothesis
Abstract
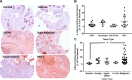
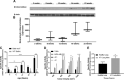
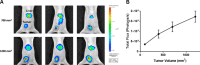
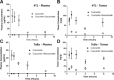
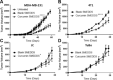
Oral consumption of curcumin, a natural polyphenol, is associated with reduced incidence of cancer. Yet, a significant amount of the orally dosed compound is eliminated in the feces, and a major fraction of the absorbed compound is metabolized to inactive glucuronides, resulting in poor bioavailability (<1%). It is not known how oral curcumin exhibits chemopreventive activity. We propose curcumin glucuronide is an inflammation-responsive natural prodrug that is converted back to curcumin on demand at the site of action. Our studies show elevated levels of β-glucuronidase, an enzyme that hydrolyzes the glycosidic bond of glucuronides to generate the parent compound, in human breast cancer. Oral administration of curcumin in mouse tumor models generated significant tumor levels of the polyphenol. Intravenous administration of the glucuronide resulted in the formation of curcumin in the tumor tissue. Chronic daily oral curcumin dosing led to tumor accumulation of curcumin and inhibition of tumor growth in tumor models with high β-glucuronidase activity. Overall, the study presented here provides preliminary evidence for a novel mechanism of action for orally administered curcumin.-Liu, G., Khanna, V., Kirtane, A., Grill, A., Panyam, J. Chemopreventive efficacy of oral curcumin: a prodrug hypothesis.
Keywords: cancer prevention; curcumin glucuronide; β-glucuronidase.
Figures


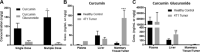
References
-
- Prasad, K. , Mantha, S. V. , Kalra, J. , and Lee, P. (1997) Prevention of hypercholesterolemic atherosclerosis by garlic, an antioxidant. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2, 309–320 - PubMed
-
- Tomren, M. A. , Másson, M. , Loftsson, T. , and Tønnesen, H. H. (2007) Studies on curcumin and curcuminoids XXXI. Symmetric and asymmetric curcuminoids: stability, activity and complexation with cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 338, 27–34 - PubMed
-
- Pan, M. H. , Huang, T. M. , and Lin, J. K. (1999) Biotransformation of curcumin through reduction and glucuronidation in mice. Drug Metab. Dispos. 27, 486–494 - PubMed
-
- Ravindranath, V. , and Chandrasekhara, N. (1980) Absorption and tissue distribution of curcumin in rats. Toxicology 16, 259–265 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

