What Factors Are Associated With Neck Fracture in One Commonly Used Bimodular THA Design? A Multicenter, Nationwide Study in Slovenia
- PMID: 31136429
- PMCID: PMC6554145
- DOI: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000646
What Factors Are Associated With Neck Fracture in One Commonly Used Bimodular THA Design? A Multicenter, Nationwide Study in Slovenia
Abstract
Background: Femoral stems with bimodular (head-neck as well as neck-body) junctions were designed to help surgeons address patients' hip anatomy individually. However, arthroplasty registers have reported higher revision rates in stems with bimodular junctions than in stems with modularity limited to the head-neck trunnion. However, to our knowledge, no epidemiologic study has identified patient-specific risk factors for modular femoral neck fractures, and some stems using these designs still are produced and marketed.
Questions/purposes: The purposes of this study were (1) to establish the survival rate free from aseptic loosening of one widely used bimodular THA design; (2) to define the proportion of patients who experienced a fracture of the stem's modular femoral neck; and (3) to determine factors associated with neck fracture.
Methods: In this retrospective, nationwide, multicenter study, we reviewed 2767 bimodular Profemur® Z stems from four hospitals in Slovenia with a mean followup of 8 years (range, 3 days to 15 years). Between 2002 and 2015, the four participating hospitals performed 26,132 primary THAs; this implant was used in 2767 of them (11%). The general indications for using this implant were primary osteoarthritis (OA) in 2198 (79%) hips and other indications in 569 (21%) hips. We followed patients from the date of the index operation to the date of death, date of revision, or the end of followup on March 1, 2018. We believe that all revisions would be captured in our sample, except for patients who may have emigrated outside the country, but the proportion of people immigrating to Slovenia is higher than the proportion of those emigrating from it; however, no formal accounting for loss to followup is possible in a study of this design. There were 1438 (52%) stems implanted in female and 1329 (48%) in male patients, respectively. A titanium alloy neck was used in 2489 hips (90%) and a cobalt-chromium neck in 278 (10%) hips. The mean body mass index (BMI) at the time of operation was 29 kg/m (SD ± 5 kg/m). We used Kaplan-Meier analysis to establish survival rates, and we performed a chart review to determine the proportion of patients who experienced femoral neck fractures. A binary logistic regression model that controlled for the potential confounding variables of age, sex, BMI, time since implantation, type of bearing, diagnosis, hospital, neck length, and neck material was used to analyze neck fractures.
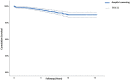
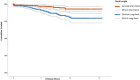
Results: There were 55 (2%) aseptic stem revisions. Survival rate free from aseptic loosening at 12 years was 97% (95% confidence interval [CI] ± 1%). Fracture of the modular neck occurred in 23 patients (0.83%) with a mean BMI of 29 kg/m (SD ± 4 kg/m.) Twenty patients with neck fractures were males and 19 of 23 fractured necks were long. Time since implantation (odds ratio [OR], 0.55; 95% CI 0.46-0.66; p < 0.001), a long neck (OR, 6.77; 95% CI, 2.1-22.2; p = 0.002), a cobalt-chromium alloy neck (OR, 5.7; 95% CI, 1.6-21.1; p = 0.008), younger age (OR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.86-0.96; p < 0.001), and male sex (OR, 3.98; 95% CI, 1.04-14.55; p = 0.043) were factors associated with neck fracture.
Conclusions: The loosening and neck fracture rates of the Profemur® Z stem were lower than in some of previously published series. However, the use of modular femoral necks in primary THA increases the risk for neck fracture, particularly in young male patients with cobalt-chromium long femoral necks. The bimodular stem we analyzed fractured unacceptably often, especially in younger male patients. For most patients, the risks of using this device outweigh the benefits, and several dozen patients had revisions and complications they would not have had if a different stem had been used.
Level of evidence: Level III, therapeutic study.
Conflict of interest statement
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and
Figures

Comment in
-
CORR Insights®: What Factors Are Associated With Neck Fracture in One Commonly Used Bimodular THA Design? A Multicenter, Nationwide Study in Slovenia.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019 Jun;477(6):1333-1334. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000708. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019. PMID: 31136430 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Aljenaei F, Catelas I, Louati H, Beaulé PE, Nganbe M. Effects of hip implant modular neck material and assembly method on fatigue life and distraction force: amterial and assembly effects on modular necks. J Orthop Res. 2017;35:2023–2030. - PubMed
-
- Atwood SA, Patten EW, Bozic KJ, Pruitt LA, Ries MD. Corrosion-induced fracture of a double-modular hip prosthesis: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92:1522–1525. - PubMed
-
- Australian Orthopaedic Association. The Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry (AOANJRR). 2018. Available at: https://aoanjrr.sahmri.com/. Accessed September 10, 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

