Phenotypic Variation in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease by Age: A Multicentre Prospective Inception Cohort Study of the Canadian Children IBD Network
- PMID: 31136648
- PMCID: PMC7242003
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjz106
Phenotypic Variation in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease by Age: A Multicentre Prospective Inception Cohort Study of the Canadian Children IBD Network
Abstract
Background and aims: Incidence of paediatric inflammatory bowel disease [IBD] in Canada is among the highest worldwide, and age of onset may be decreasing. In a multicentre nationwide inception cohort study, we examined variation in phenotype of IBD throughout the paediatric age spectrum.
Methods: Children aged ≥2 years [y] and <17y [A1 age at diagnosis], with new onset IBD, were systematically evaluated at sites of the Canadian Children IBD Network. Prospectively recorded phenotypic data were compared between age groups.
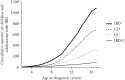
Results: Among 1092 children (70% Caucasian; 64% Crohn's disease [CD], 36% ulcerative colitis/inflammatory bowel disease unclassified [UC/IBD-U]; median age 13 y, interquartile range [IQR] 11-15 y), 210 [19%] were diagnosed before the age of age 10 y [Paris A1a] and 43 [4%] before age 6 y (very-early-onset [VEO-IBD]). CD was less common in younger children [42%, 56%, 66%, respectively, of VEO-IBD, A1a; A1b]. Colon-only IBD [UC/IBDU or CD-colon] was present in 81% of VEO-IBD and 65% of A1a; ileal disease increased progressively, reaching plateau at age 10 y. CD location was ileocolonic [L3] in 53% overall. Ileitis [L1] increased with age [6% of VEO-IBD; 13% of A1a; 21% of A1b], as did stricturing/penetrating CD [4% of A1a; 11% of A1b]. At all ages UC was extensive [E3/E4] in >85%, and disease activity moderate to severe according to Physician's Global Assessment [PGA] and weighted Paediatric Crohn's Disease Activity Index/Paediatric Ulcerative Colitis Activity Index [wPCDAI/PUCAI] in >70%. Heights were modestly reduced in CD [mean height z score -0.30 ± 1.23], but normal in UC/IBD-U.
Conclusions: Paris classification of age at diagnosis is supported by age-related increases in ileal disease until age 10 years. Other phenotypic features, including severity, are similar across all ages. Linear growth is less impaired in CD than in historical cohorts, reflecting earlier diagnosis.
Keywords: IBD; paediatrics; phenotype.
Copyright © 2019 European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, et al. . Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 2018;390:2769–78. - PubMed
-
- Benchimol EI, Fortinsky KJ, Gozdyra P, Van den Heuvel M, Van Limbergen J, Griffiths AM. Epidemiology of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review of international trends. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2011;17:423–39. - PubMed
-
- Perminow G, Brackmann S, Lyckander LG, et al. ; IBSEN-II Group A characterization in childhood inflammatory bowel disease, a new population-based inception cohort from South-Eastern Norway, 2005-07, showing increased incidence in Crohn’s disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 2009;44:446–56. - PubMed
-
- Levine A, Griffiths A, Markowitz J, et al. . Pediatric modification of the Montreal classification for inflammatory bowel disease: the Paris classification. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2011;17:1314–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

