Jasmonic Acid Signaling Pathway in Plants
- PMID: 31137463
- PMCID: PMC6566436
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20102479
Jasmonic Acid Signaling Pathway in Plants
Abstract
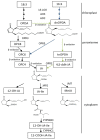
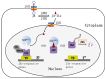
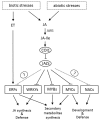
Jasmonic acid (JA) and its precursors and dervatives, referred as jasmonates (JAs) are important molecules in the regulation of many physiological processes in plant growth and development, and especially the mediation of plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. JAs biosynthesis, perception, transport, signal transduction and action have been extensively investigated. In this review, we will discuss the initiation of JA signaling with a focus on environmental signal perception and transduction, JA biosynthesis and metabolism, transport of signaling molecules (local transmission, vascular bundle transmission, and airborne transportation), and biological function (JA signal receptors, regulated transcription factors, and biological processes involved).
Keywords: biological function; environmental response; jasmonic acid; signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mur L.A., Kenton P., Atzorn R., Miersch O., Wasternack C. The outcomes of concentration—Specific interactions between salicylate and jasmonate signaling include synergy, antagonism, and oxidative stress leading to cell death. Plant Physiol. 2006;140:249–262. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.072348. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gupta A., Hisano H., Hojo Y., Matsuura T., Ikeda Y., Mori I.C., Kumar M.S. Global profiling of phytohormone dynamics during combined drought and pathogen stress in Arabidopsis thaliana reveals ABA and JA as major regulators. Sci. Rep-UK. 2017;7:4017. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03907-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

