Virtual Screening Guided Design, Synthesis and Bioactivity Study of Benzisoselenazolones (BISAs) on Inhibition of c-Met and Its Downstream Signalling Pathways
- PMID: 31137515
- PMCID: PMC6566228
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20102489
Virtual Screening Guided Design, Synthesis and Bioactivity Study of Benzisoselenazolones (BISAs) on Inhibition of c-Met and Its Downstream Signalling Pathways
Abstract
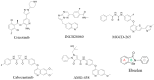
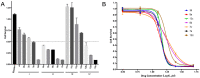
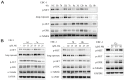
c-Met is a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase and an important therapeutic target for anticancer drugs. In this study, we designed a small library containing 300 BISAs molecules that consisted of carbohydrates, amino acids, isothiourea, tetramethylthiourea, guanidine and heterocyclic groups and screened c-Met targeting compounds using docking and MM/GBSA. Guided by virtual screening, we synthesised a series of novel compounds and their activity on inhibition of the autophosphorylation of c-Met and its downstream signalling pathway proteins were evaluated. We found a panel of benzisoselenazolones (BISAs) obtained by introducing isothiourea, tetramethylthiourea and heterocyclic groups into the C-ring of Ebselen, including 7a, 7b, 8a, 8b and 12c (with IC50 values of less than 20 μM in MET gene amplified lung cancer cell line EBC-1), exhibited more potent antitumour activity than Ebselen by cell growth assay combined with in vitro biochemical assays. In addition, we also tested the antitumour activity of three cancer cell lines without MET gene amplification/activation, including DLD1, MDA-MB-231 and A549. The neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells with HGF overexpression which activates MET signalling are sensitive to MET inhibitors. The results reveal that our compounds may be nonspecific multitarget kinase inhibitors, just like type-II small molecule inhibitors. Western blot analysis showed that these inhibitors inhibited autophosphorylation of c-MET, and its downstream signalling pathways, such as PI3K/AKT and MARK/ERK. Results suggest that bensoisoselenones can be used as a scaffold for the design of c-Met inhibiting drug leads, and this study opens up new possibilities for future antitumour drug design.
Keywords: benzoisoselenone; c-Met inhibition; docking; molecular dynamics simulation; virtual screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synthesis of novel 6,7-dimethoxy-4-anilinoquinolines as potent c-Met inhibitors.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019 Dec;34(1):124-133. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2018.1533822. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30422010 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and molecular modeling studies of new series of antitumor 1,2,4-triazines with potential c-Met kinase inhibitory activity.Bioorg Chem. 2018 Feb;76:154-165. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2017.11.006. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Bioorg Chem. 2018. PMID: 29175587
-
Design, synthesis and antitumor evaluation of novel 5-methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives as potential c-Met inhibitors.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Nov;104:104356. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104356. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 33142417
-
Recent Advances in the Design and Synthesis of c-Met Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents (2014-Present).Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(1):57-64. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666161028161441. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27804876 Review.
-
Recent advances in the discovery of small molecule c-Met Kinase inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jan 1;143:1103-1138. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.08.044. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29157685 Review.
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal Epithelial Transition Factor Signaling in Pediatric Nervous System Tumors: Implications for Malignancy and Cancer Stem Cell Enrichment.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 13;9:654103. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.654103. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34055785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large-Scale Virtual Screening Against the MET Kinase Domain Identifies a New Putative Inhibitor Type.Molecules. 2020 Feb 19;25(4):938. doi: 10.3390/molecules25040938. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32093126 Free PMC article.
-
A c-Met Inhibitor Suppresses Osteosarcoma Progression via the ERK1/2 Pathway in Human Osteosarcoma Cells.Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Sep 10;14:4791-4804. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S317122. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 34531665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zou H.Y., Li Q., Lee J.H., Arango M.E., McDonnell S.R., Yamazaki S., Koudriakova T.B., Alton G., Cui J.J., Kung P.P., et al. An Orally Available Small-Molecule Inhibitor of c-Met, PF-2341066, Exhibits Cytoreductive Antitumor Efficacy through Antiproliferative and Antiangiogenic Mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2007;67:4408–4417. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4443. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2018ZX09735-004/National Science and Technology Major Project of China
- U1706213 and U1406403/NSFC-Shandong Joint Fund
- No.2015ASKJ02/Innovation Project from Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology
- No. 2018SDKJ0403/Marine S&T Fund of Shandong Province for Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology(Qingdao)
- No. 201762011 for R.Y./Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

