CO-Releasing Materials: An Emphasis on Therapeutic Implications, as Release and Subsequent Cytotoxicity Are the Part of Therapy
- PMID: 31137526
- PMCID: PMC6566563
- DOI: 10.3390/ma12101643
CO-Releasing Materials: An Emphasis on Therapeutic Implications, as Release and Subsequent Cytotoxicity Are the Part of Therapy
Abstract
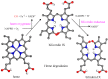
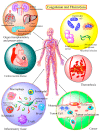
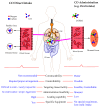
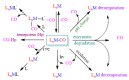
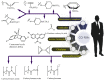
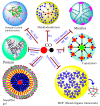
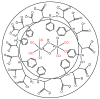
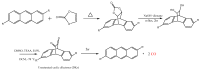
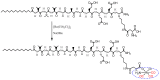
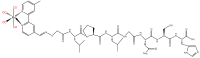
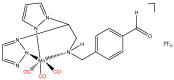
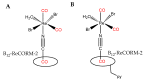
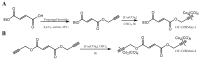
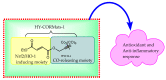
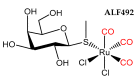
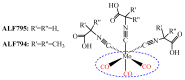
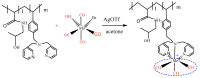
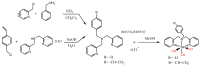
The CO-releasing materials (CORMats) are used as substances for producing CO molecules for therapeutic purposes. Carbon monoxide (CO) imparts toxic effects to biological organisms at higher concentration. If this characteristic is utilized in a controlled manner, it can act as a cell-signaling agent for important pathological and pharmacokinetic functions; hence offering many new applications and treatments. Recently, research on therapeutic applications using the CO treatment has gained much attention due to its nontoxic nature, and its injection into the human body using several conjugate systems. Mainly, there are two types of CO insertion techniques into the human body, i.e., direct and indirect CO insertion. Indirect CO insertion offers an advantage of avoiding toxicity as compared to direct CO insertion. For the indirect CO inhalation method, developers are facing certain problems, such as its inability to achieve the specific cellular targets and how to control the dosage of CO. To address these issues, researchers have adopted alternative strategies regarded as CO-releasing molecules (CORMs). CO is covalently attached with metal carbonyl complexes (MCCs), which generate various CORMs such as CORM-1, CORM-2, CORM-3, ALF492, CORM-A1 and ALF186. When these molecules are inserted into the human body, CO is released from these compounds at a controlled rate under certain conditions or/and triggers. Such reactions are helpful in achieving cellular level targets with a controlled release of the CO amount. However on the other hand, CORMs also produce a metal residue (termed as i-CORMs) upon degradation that can initiate harmful toxic activity inside the body. To improve the performance of the CO precursor with the restricted development of i-CORMs, several new CORMats have been developed such as micellization, peptide, vitamins, MOFs, polymerization, nanoparticles, protein, metallodendrimer, nanosheet and nanodiamond, etc. In this review article, we shall describe modern ways of CO administration; focusing primarily on exclusive features of CORM's tissue accumulations and their toxicities. This report also elaborates on the kinetic profile of the CO gas. The comprehension of developmental phases of CORMats shall be useful for exploring the ideal CO therapeutic drugs in the future of medical sciences.
Keywords: CO administration; CO kinetic profile; CO-releasing materials; CO-releasing molecules; cellular targets; heme oxygenase; organometallic complexes; pathological role; pharmaceutical drugs; pharmacokinetic functions; therapeutic agent.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of the paper.
Figures


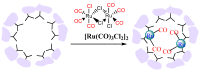

Similar articles
-
Water-Soluble Carbon Monoxide-Releasing Molecules (CORMs).Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2022 Dec 14;381(1):3. doi: 10.1007/s41061-022-00413-6. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2022. PMID: 36515756 Review.
-
Examining the antimicrobial activity and toxicity to animal cells of different types of CO-releasing molecules.Dalton Trans. 2016 Jan 28;45(4):1455-66. doi: 10.1039/c5dt02238j. Dalton Trans. 2016. PMID: 26673556
-
Development of Triggerable, Trackable, and Targetable Carbon Monoxide Releasing Molecules.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Oct 20;53(10):2273-2285. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00402. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 32929957 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of frequently applied carbon monoxide releasing molecules (CORMs) in typical CO-sensitive model systems - A comparative in vitro study.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Jul 15;687:108383. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108383. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 32335048
-
Controlled therapeutic delivery of CO from carbon monoxide-releasing molecules (CORMs).J Control Release. 2022 Oct;350:652-667. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.08.055. Epub 2022 Sep 7. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 36063960 Review.
Cited by
-
Tricarbonyl-Pyrazine-Molybdenum(0) Metal-Organic Frameworks for the Storage and Delivery of Biologically Active Carbon Monoxide.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023 Apr 10;9(4):1909-1918. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.3c00140. Epub 2023 Mar 30. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023. PMID: 36996427 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in carbon monoxide-releasing nanomaterials.Bioact Mater. 2024 Mar 14;37:30-50. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.03.001. eCollection 2024 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 38515608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Intercalation of CORM-2 with Pharmaceutical Clay Montmorillonite (MMT) Aids for Therapeutic Carbon Monoxide Release.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 14;20(14):3453. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143453. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31337099 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing Gasotransmitters to Combat Age-Related Oxidative Stress in Smooth Muscle and Endothelial Cells.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 27;18(3):344. doi: 10.3390/ph18030344. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40143122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential effects of carbon monoxide donor and its nanoparticles on experimentally induced gastric ulcer in rats.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Jun;31(3):1495-1510. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01166-4. Epub 2023 Mar 8. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36882659 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tenhunen R., Marver H.S., Schmid R. Microsomal heme oxygenase. Characterization of the enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1969;244:6388–6394. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

