The Characteristics of PD-L1 Inhibitors, from Peptides to Small Molecules
- PMID: 31137573
- PMCID: PMC6572691
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24101940
The Characteristics of PD-L1 Inhibitors, from Peptides to Small Molecules
Abstract
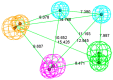
The programmed cell death ligand protein 1 (PD-L1) is a member of the B7 protein family and consists of 290 amino acid residues. The blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint pathway is effective in tumor treatment. Results: Two pharmacophore models were generated based on peptides and small molecules. Hypo 1A consists of one hydrogen bond donor, one hydrogen bond acceptor, two hydrophobic points and one aromatic ring point. Hypo 1B consists of one hydrogen bond donor, three hydrophobic points and one positive ionizable point. Conclusions: The pharmacophore model consisting of a hydrogen bond donor, hydrophobic points and a positive ionizable point may be helpful for designing small-molecule inhibitors targeting PD-L1.
Keywords: peptide; pharmacophore; programmed cell death ligand protein 1; small molecule.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures











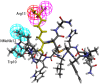
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

