Quality and Authenticity Control of Functional Red Yeast Rice-A Review
- PMID: 31137594
- PMCID: PMC6572552
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24101944
Quality and Authenticity Control of Functional Red Yeast Rice-A Review
Abstract
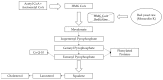
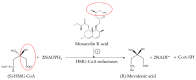
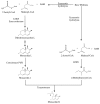
Red yeast rice (RYR) is made by fermenting the rice with Monascus. It is commonly used in food colorants, dyeing, and wine making in China and its neighboring countries. Nowadays RYR has two forms on the market: common RYR is used for food products, the other form is functional RYR for medicine. However, some researchers reported that commercial lovastatin (structure is consistent with monacolin K) is illegally added to common RYR to meet drug quality standards, so as to imitate functional RYR and sell the imitation at a higher price. Based on current detection methods, it is impossible to accurately distinguish whether functional RYR is adulterated. Therefore, it is especially important to find a way to authenticate functional RYR. In the current review, the advances in history, applications, components (especially monacolins, monacolins detection methods), quality standards, authentication methods and perspectives for the future study of RYR are systematically reviewed.
Keywords: authentication methods; detection methods; functional RYR; monacolin K; quality standards.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chemical profiling and quantification of monacolins and citrinin in red yeast rice commercial raw materials and dietary supplements using liquid chromatography-accurate QToF mass spectrometry: Chemometrics application.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Nov;100:243-253. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.07.039. Epub 2014 Aug 9. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 25168220
-
Stable isotope ratio analysis for authentication of red yeast rice.Talanta. 2017 Nov 1;174:228-233. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.05.057. Epub 2017 May 23. Talanta. 2017. PMID: 28738573
-
[Suggestions for revision of quality standards of red yeast rice for medicinal and edible purposes in China].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Oct;49(20):5659-5673. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240715.601. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39701748 Review. Chinese.
-
Marked variability of monacolin levels in commercial red yeast rice products: buyer beware!Arch Intern Med. 2010 Oct 25;170(19):1722-7. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2010.382. Arch Intern Med. 2010. PMID: 20975018
-
Functional food red yeast rice (RYR) for metabolic syndrome amelioration: a review on pros and cons.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 May;32(5):87. doi: 10.1007/s11274-016-2035-2. Epub 2016 Apr 2. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27038957 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of an Improved Menopausal Symptom-Alleviating Licorice (Glycyrrhiza uralensis) by Biotransformation Using Monascus albidulus.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Feb 28;30(2):178-186. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1909.09037. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31752065 Free PMC article.
-
Nutraceutical Combinations in Hypercholesterolemia: Evidence from Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials.Nutrients. 2021 Sep 8;13(9):3128. doi: 10.3390/nu13093128. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34579005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Investigation of Lipid Profile During the Solid-State Fermentation of Rice by Monascus purpureus.Foods. 2025 Feb 6;14(3):537. doi: 10.3390/foods14030537. Foods. 2025. PMID: 39942130 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of NaTto Red Yeast Rice on Regulating Blood Lipid (ENTRY) Study: A Multicenter, Double-Placebo, Double-Blinded, Randomized Controlled Trial in Chinese Adults.Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2025 Apr 24;11(2):122-129. doi: 10.1002/cdt3.70005. eCollection 2025 Jun. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40486958 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Monacolins and Berberine in Food Supplements for Lipid Control: An Overview of Products Sold on the Italian Market.Molecules. 2021 Apr 12;26(8):2222. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082222. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33921464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ozlem T., Sebile A. A review on the red yeast rice (Monascus purpureus) Turk. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2004;2:37–49.
-
- Chen W., He Y., Zhou Y., Shao Y., Feng Y., Li M., Chen F. Edible Filamentous Fungi from the Species Monascus: Early Traditional Fermentations, Modern Molecular Biology, and Future Genomics. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015;14:555–567. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12145. - DOI
-
- Lin F. Textual research on Gutian as place where red yeast rice originated. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 2017;48:2793–2800.
-
- Rojsuntornkitti K., Jittrepotch N., Kongbangkerd T., Kraboun K. Substitution of nitrite by Chinese red broken rice powder in Thaitraditional fermented pork sausage (Nham) Int. Food Res. J. 2010;17:153–161.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

