The Roles of Hippo Signaling Transducers Yap and Taz in Chromatin Remodeling
- PMID: 31137701
- PMCID: PMC6562424
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8050502
The Roles of Hippo Signaling Transducers Yap and Taz in Chromatin Remodeling
Abstract
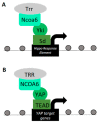
Hippo signaling controls cellular processes that ultimately impact organogenesis and homeostasis. Consequently, disease states including cancer can emerge when signaling is deregulated. The major pathway transducers Yap and Taz require cofactors to impart transcriptional control over target genes. Research into Yap/Taz-mediated epigenetic modifications has revealed their association with chromatin-remodeling complex proteins as a means of altering chromatin structure, therefore affecting accessibility and activity of target genes. Specifically, Yap/Taz have been found to associate with factors of the GAGA, Ncoa6, Mediator, Switch/sucrose nonfermentable (SWI/SNF), and Nucleosome Remodeling and Deacetylase (NuRD) chromatin-remodeling complexes to alter the accessibility of target genes. This review highlights the different mechanisms by which Yap/Taz collaborate with other factors to modify DNA packing at specific loci to either activate or repress target gene transcription.
Keywords: Hippo pathway; chromatin; epigenetic; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

