Influence of intermittent fasting on myocardial infarction-induced cardiac remodeling
- PMID: 31138145
- PMCID: PMC6540428
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-019-1113-4
Influence of intermittent fasting on myocardial infarction-induced cardiac remodeling
Abstract
Background: Information on the role of intermittent fasting (IF) on pathologic cardiac remodeling is scarce. We compared the effects of IF before and after myocardial infarction (MI) on rat cardiac remodeling and survival.
Methods: Wistar rats were intermittently fasted (food available every other day) or fed ad libitum for 12 weeks and then divided into three groups: AL - fed ad libitum; AL/IF - fed AL before MI and IF after MI; and IF - fed IF before and after MI. Echocardiogram was performed before MI and 2 and 12 weeks after surgery. Isolated hearts were evaluated in Langendorff preparations.
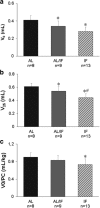
Results: Before surgery, body weight (BW) was lower in IF than AL. Final BW was lower in AL/IF and IF than AL. Perioperative mortality did not change between AL (31.3%) and IF (27.3%). Total mortality was lower in IF than AL. Before surgery, echocardiographic parameters did not differ between groups. Two weeks after surgery, MI size did not differ between groups. Twelve weeks after MI, left ventricular (LV) diastolic posterior wall thickness was lower in AL/IF and IF than AL. The percentage of variation of echocardiographic parameters between twelve and two weeks showed that MI size decreased in all groups and the reduction was higher in IF than AL/IF. In Langendorff preparations, LV volume at zero end-diastolic pressure (V0; AL: 0.41 ± 0.05; AL/IF: 0.34 ± 0.06; IF: 0.28 ± 0.05 mL) and at 25 mmHg end-diastolic pressure (V25; AL: 0.61 ± 0.05; AL/IF: 0.54 ± 0.07; IF: 0.44 ± 0.06 mL) was lower in AL/IF and IF than AL and V25 was lower in IF than AL/IF. V0/BW ratio was lower in IF than AL and LV weight/V0 ratio was higher in IF than AL. Myocyte diameter was lower in AL/IF and IF than AL (AL: 17.3 ± 1.70; AL/IF: 15.1 ± 2.21; IF: 13.4 ± 1.49 μm). Myocardial hydroxyproline concentration and gene expression of ANP, Serca 2a, and α- and β-myosin heavy chain did not differ between groups.
Conclusion: Intermittent fasting initiated before or after MI reduces myocyte hypertrophy and LV dilation. Myocardial fibrosis and fetal gene expression are not modulated by feeding regimens. Benefit is more evident when intermittent fasting is initiated before rather than after MI.
Keywords: Calorie restriction; Echocardiogram; Fetal gene expression; Heart failure; Intermittent feeding; Isolated heart; Langendorff preparation; Myocardial infarction; Rat; Ventricular remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- St-Onge MP, Ard J, Baskin ML, et al. American Heart Association obesity Committee of the Council on lifestyle and Cardiometabolic health; council on cardiovascular disease in the young; council on clinical cardiology; and stroke council. Meal timing and frequency: implications for cardiovascular disease prevention. A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;135:e96–e121. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000476. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

