Efficient disruption of bcr-abl gene by CRISPR RNA-guided FokI nucleases depresses the oncogenesis of chronic myeloid leukemia cells
- PMID: 31138265
- PMCID: PMC6537404
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1229-5
Efficient disruption of bcr-abl gene by CRISPR RNA-guided FokI nucleases depresses the oncogenesis of chronic myeloid leukemia cells
Abstract
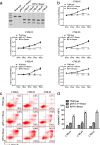
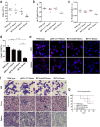
Background: The bcr-abl fusion gene encodes BCR-ABL oncoprotein and plays a crucial role in the leukemogenesis of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Current therapeutic methods have limited treatment effect on CML patients with drug resistance or disease relapse. Therefore, novel therapeutic strategy for CML is essential to be explored and the CRISPR RNA-guided FokI nucleases (RFNs) meet the merits of variable target sites and specificity of cleavage enabled its suitability for gene editing of CML. The RFNs provide us a new therapeutic direction to obliterate this disease.
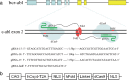
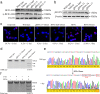
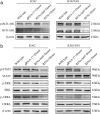
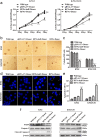
Methods: Guide RNA (gRNA) expression plasmids were constructed by molecular cloning technique. The modification rate of RFNs on bcr-abl was detected via NotI restriction enzyme digestion and T7 endonuclease 1 (T7E1) assay. The expression of BCR-ABL and its downstream signaling molecules were determined by western blotting. The effects of RFNs on cell proliferation and apoptosis of CML cell lines and CML stem/progenitor cells were evaluated by CCK-8 assay and flow cytometry. In addition, murine xenograft model was adopted to evaluate the capacity of RFNs in attenuating the tumorigenic ability of bcr-abl.
Results: The RFNs efficiently disrupted bcr-abl and prematurely terminated its translation. The destruction of bcr-abl gene suppressed cell proliferation and induced cell apoptosis in CML lines and in CML stem/progenitor cells. Moreover, the RFNs significantly impaired the leukemogenic capacity of CML cells in xenograft model.
Conclusion: These results illustrate that the RFNs can target to disrupt bcr-abl gene and may provide a new therapeutic option for CML patients affiliated by drug resistance or disease relapse.
Keywords: Bcr-abl; Chronic myeloid leukemia; Homology-directed repair; Leukemogenesis; RNA guided-FokI nucleases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of apoptosis in imatinib sensitive and resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells by efficient disruption of bcr-abl oncogene with zinc finger nucleases.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Mar 20;37(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0732-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29554925 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted disruption of the BCR-ABL fusion gene by Cas9/dual-sgRNA inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia cells.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Apr 25;56(4):525-537. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2023280. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 38414349 Free PMC article.
-
The CRISPR/Cas9 system efficiently reverts the tumorigenic ability of BCR/ABL in vitro and in a xenograft model of chronic myeloid leukemia.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 18;8(16):26027-26040. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15215. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28212528 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic myelogenous leukemia as a paradigm of early cancer and possible curative strategies.Leukemia. 2003 Jul;17(7):1211-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402912. Leukemia. 2003. PMID: 12835715 Review.
-
Preclinical approaches in chronic myeloid leukemia: from cells to systems.Exp Hematol. 2017 Mar;47:13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Exp Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28017647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CRISPR/Cas9 Landscape: Current State and Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 8;24(22):16077. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216077. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular delivery of anti-BCR/ABL antibody by PLGA nanoparticles suppresses the oncogenesis of chronic myeloid leukemia cells.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Sep 6;14(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01150-x. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34488814 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-Cas9 in basic and translational aspects of cancer therapy.Bioimpacts. 2024;14(6):30087. doi: 10.34172/bi.2024.30087. Epub 2024 Mar 10. Bioimpacts. 2024. PMID: 39493894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRIB2 regulates the expression of miR‑33a‑5p through the ERK/c‑Fos pathway to affect the imatinib resistance of chronic myeloid leukemia cells.Int J Oncol. 2022 May;60(5):49. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5339. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Int J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35302171 Free PMC article.
-
Manipulating the NKG2D Receptor-Ligand Axis Using CRISPR: Novel Technologies for Improved Host Immunity.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 12;12:712722. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.712722. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34456921 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

