Gain-of-function mutations in a member of the Src family kinases cause autoinflammatory bone disease in mice and humans
- PMID: 31138708
- PMCID: PMC6575637
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1819825116
Gain-of-function mutations in a member of the Src family kinases cause autoinflammatory bone disease in mice and humans
Abstract
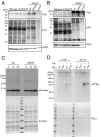
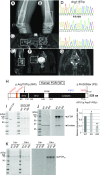
Autoinflammatory syndromes are characterized by dysregulation of the innate immune response with subsequent episodes of acute spontaneous inflammation. Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CRMO) is an autoinflammatory bone disorder that presents with bone pain and localized swelling. Ali18 mice, isolated from a mutagenesis screen, exhibit a spontaneous inflammatory paw phenotype that includes sterile osteomyelitis and systemic reduced bone mineral density. To elucidate the molecular basis of the disease, positional cloning of the causative gene for Ali18 was attempted. Using a candidate gene approach, a missense mutation in the C-terminal region of Fgr, a member of Src family tyrosine kinases (SFKs), was identified. For functional confirmation, additional mutations at the N terminus of Fgr were introduced in Ali18 mice by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing. N-terminal deleterious mutations of Fgr abolished the inflammatory phenotype in Ali18 mice, but in-frame and missense mutations in the same region continue to exhibit the phenotype. The fact that Fgr null mutant mice are morphologically normal suggests that the inflammation in this model depends on Fgr products. Furthermore, the levels of C-terminal negative regulatory phosphorylation of Fgr Ali18 are distinctly reduced compared with that of wild-type Fgr. In addition, whole-exome sequencing of 99 CRMO patients including 88 trios (proband and parents) identified 13 patients with heterozygous coding sequence variants in FGR, including two missense mutant proteins that affect kinase activity. Our results strongly indicate that gain-of-function mutations in Fgr are involved in sterile osteomyelitis, and thus targeting SFKs using specific inhibitors may allow for efficient treatment of the disease.
Keywords: autoinflammation; bone destruction; chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis; mouse model; tyrosine kinase.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Jansson A., et al. , Classification of non-bacterial osteitis: Retrospective study of clinical, immunological and genetic aspects in 89 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46, 154–160 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Roderick M. R., Sen E. S., Ramanan A. V., Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis in children and adults: Current understanding and areas for development. Rheumatology (Oxford) 57, 41–48 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

