Elevated microRNA-145 inhibits the development of oral squamous cell carcinoma through inactivating ERK/MAPK signaling pathway by down-regulating HOXA1
- PMID: 31138758
- PMCID: PMC6591566
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20182214
Elevated microRNA-145 inhibits the development of oral squamous cell carcinoma through inactivating ERK/MAPK signaling pathway by down-regulating HOXA1
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Elevated microRNA-145 inhibits the development of oral squamous cell carcinoma through inactivating ERK/MAPK signaling pathway by down-regulating HOXA1.Biosci Rep. 2022 Nov 30;42(11):BSR-2018-2214_RET. doi: 10.1042/BSR-2018-2214_RET. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36354012 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: Elevated microRNA-145 inhibits the development of oral squamous cell carcinoma through inactivating ERK/MAPK signaling pathway by down-regulating HOXA1.Biosci Rep. 2022 Sep 30;42(9):BSR-2018-2214_EOC. doi: 10.1042/BSR-2018-2214_EOC. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36156069 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
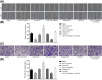
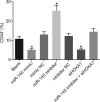
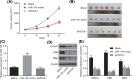
Background: Oral cancer is one of the most frequent solid cancers worldwide, and oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) constitutes approximately 90% of oral cancers. The discovery of reliable prognostic indicators would be a potential strategy for OSCC treatment. In the present study, we aim to explore the underlying mechanism by which microRNA-145 (miR-145) affected OSCC. Methods: Forty-eight patients diagnosed with OSCC were enrolled to obtain the OSCC tissues and adjacent normal tissues. The targeting relationship between miR-145 and Homeobox A1 (HOXA1) was verified. In order to assess the effects of miR-145 in OSCC and the detailed regulatory mechanism, the SCC-9 cell line was adopted, in which expression of miR-145 and HOXA1 were altered by transfection. Then, a series of in vitro and in vivo experiments were performed to evaluate the cell viability, migration, invasion, and tumor growth. Results: miR-145 was poorly expressed and HOXA1 was highly expressed in OSCC. HOXA1 was verified as a target of miR-145 to mediate the activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen activated protein kinase (ERK/MAPK) signaling pathway. In the circumstance of miR-145 elevation or HOXA1 depletion, the SCC-9 cell line manifested with inhibited cell viability, invasion, and migration in vitro, coupled with reduced tumor growth in vivo, with a decreased expression of ERK/MAPK signaling pathway-related genes/proteins. Conclusion: These findings suggested that miR-145 can inhibit HOXA1 to inactivate the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway, thereby suppressing OSCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion to further inhibit the development of OSCC, highlighting a novel therapeutic target for the OSCC treatment.
Keywords: Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase/mitogen activated protein kinase; Homeobox A1; MicroRNA-145; Oral squamous cell carcinoma.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures




References
-
- Agnihotri N.S. and Astekar M. (2018) The role of novel prognostic markers PROX1 and FOXC2 in carcinogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 12, 171–184 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

